STAMLO 10 Tablet
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
Dr. REDDY'S LABORATORIES LTD, India
ក្រុមហ៊ុនចែកចាយឱសថនៅប្រទេសកម្ពុជា:
DKSH


- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
Amlodipine 10mg
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
For the treatment of :
- hypertension,
- chronic stable angina pectoris,
- vasospastic (Prinzmetal’s) angina.
Dosage
For oral use
Adults
For both hypertension and angina the usual initial dose is 5mg of amlodipine besylate once daily which may be increased to a maximum dose of 10mg depending on the individual patient’s response.
In hypertensive patients, amlodipine has been used in combination with a thiazide diuretic, alpha blocker, beta blocker, or an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. For angina, amlodipine may be used as monotherapy or in combination with other anti-anginal medicinal products in patients with angina that is refractory to nitrates and/or to adequate doses of beta blockers.
No dose adjustment of amlodipine is required upon concomitant administration of thiazide diuretics, beta blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
Children
Children under 6 years of age
There are no relevant data available.
Children and adolescents from 6 years to 17 years of age
The recommended antihypertensive oral dose in paediatric patients ages 6-17 years is 2.5mg once daily as a starting dose, up-titrated to 5mg once daily if the blood pressure goal is not achieved after 4 weeks. Doses in excess of 5mg daily have not been studied in paediatric patients.
Elderly
Amlodipine used at similar doses in elderly or younger patients is equally well tolerated. Normal dosage regimens are recommended in the elderly, but increase of the dosage should take place with dare.
Renal impairment
Changes in amlodipine plasma concentrations are not correlated with degree of renal impairment, therefore the normal dosage is recommended. Amlodipine is not dialyzable.
Hepatic impairment
Dosage recommendations have not been established in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment; therefore dose selection should be cautious and should start at the lower end of the dosing range. The pharmacokinetics of amlodipine have not been studied in severe hepatic impairment. Amlodipine should be initiated at the lowest dose and titrated slowly in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
-
ហាមប្រើ
- hypersensitivity to dihydropridine derivatives, amlodipine or to any of the excipients,
- severe hypotension,
- shock (including cardiogenic shock),
- obstruction of the outflow tract of the left ventricle (e.g., high grade aortic stenosis),
- haemodynamically unstable heart failure after acute myocardial infarction.
-
ផលរំខាន
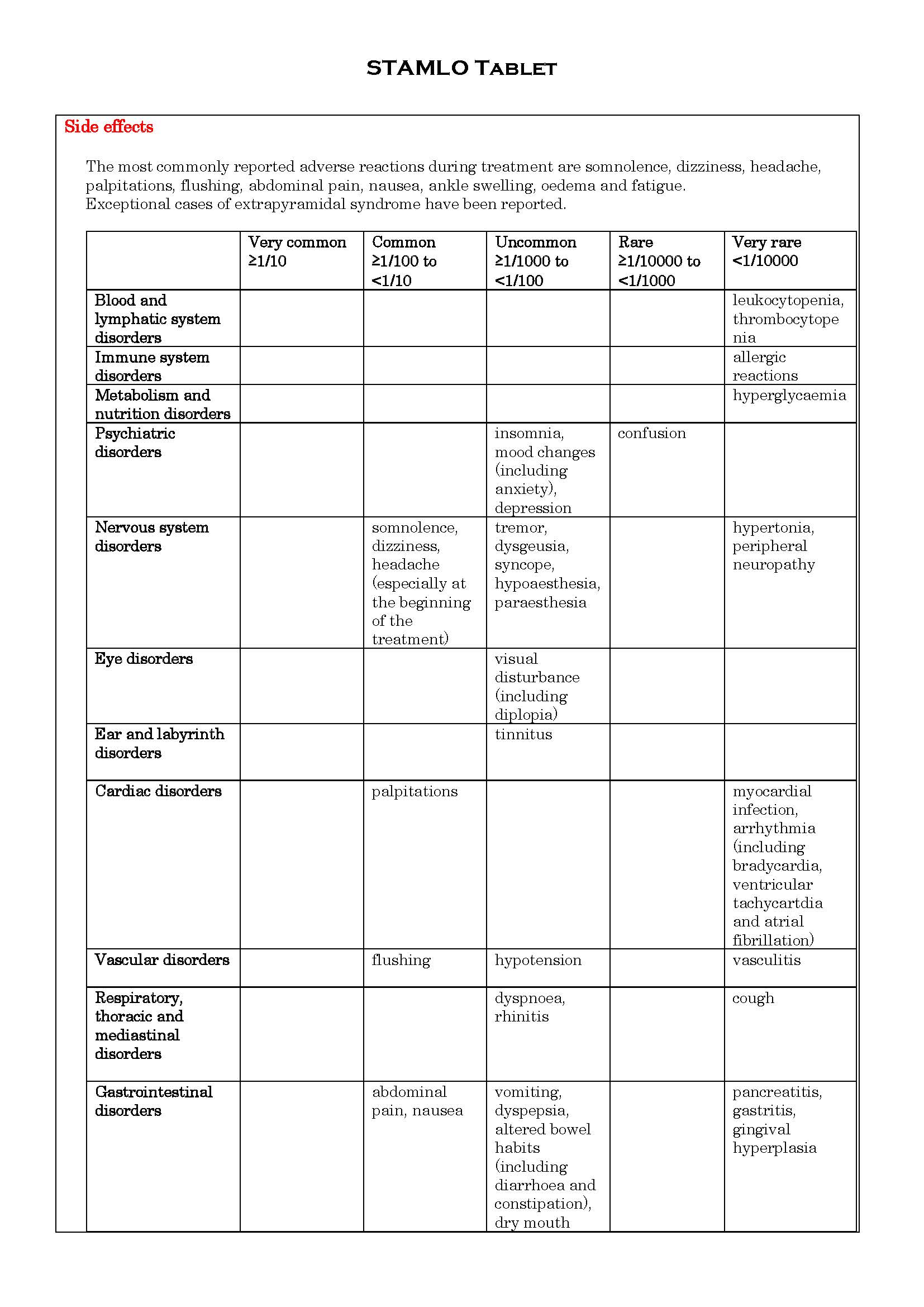
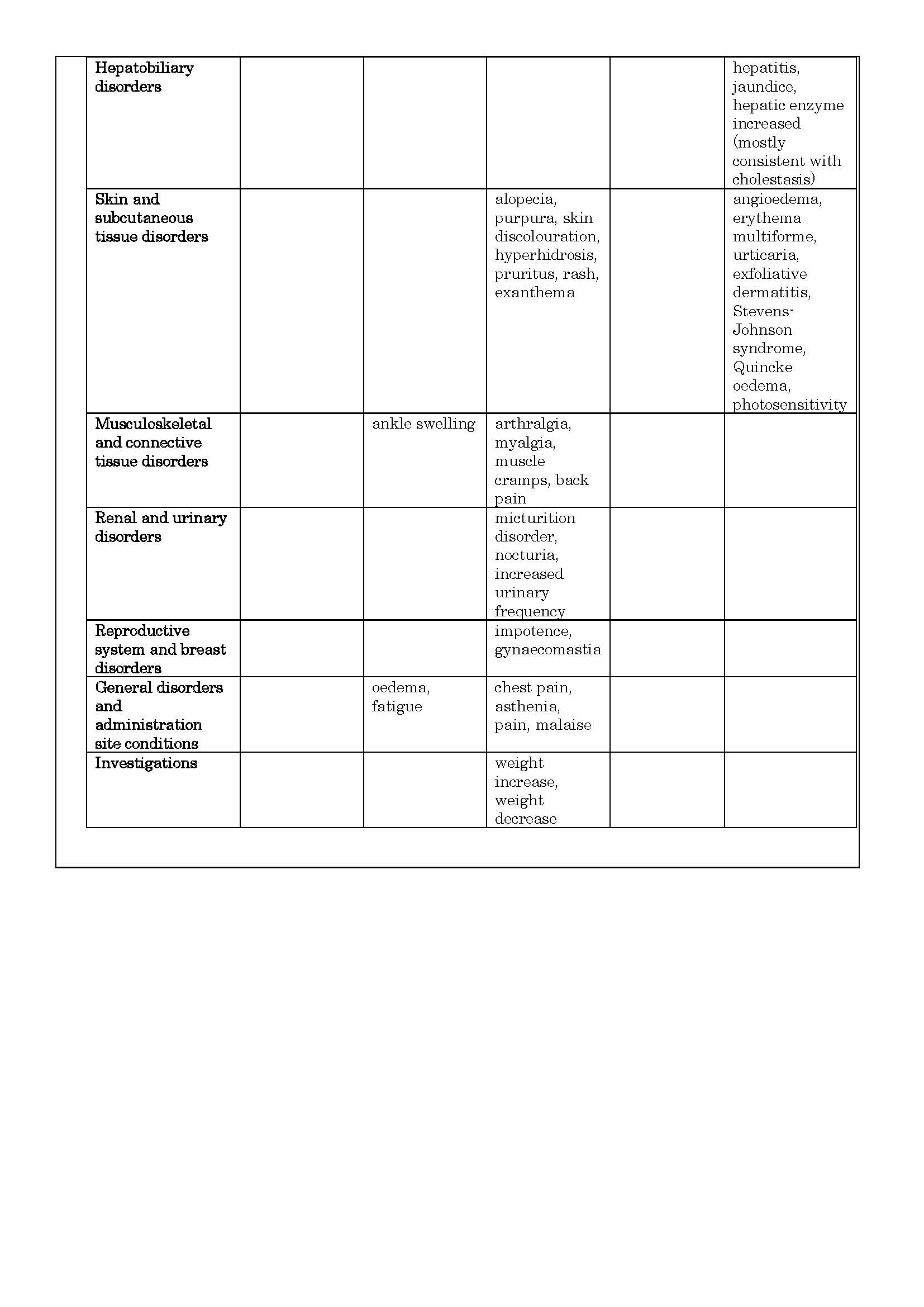
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
CYP3A4 inhibitors
Concomitant use of amlodipine with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (protease inhibitors, azole antifungals, macrolides like erythromycin or clarithromycin, verapamil of diltiazem) may give rise to significant increase in amlodipine exposure. The clinical translation of these PK variations may be more pronounced in the elderly. Clinical monitoring and dose adjustment may thus be required.
CYP3A4 inducers
There is no data available regarding the effect of CYP3A4 inducers on amlodipine. The concomitant use of CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampicin, hypericum perforatum) may give a lower plasma concentration of amlodipine. Amlodipine should be used with caution together with CYP3A4 inducers.
Grapefruit/ grapefruit juice
Administration of amlodipine with grapefruit or grapefruit juice is not recommended as bioavailability may be increased in some patients resulting in increased blood pressure lowering effects.
Dantrolene (infusion)
In animals, lethal ventricular fibrillation and cardiovascular collapse are observed in association with hyperkalaemia after administration of verapamil and intravenous dantrolene. Due to risk hyperkalaemia, it is recommended that the co-administration of calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine be avoided in patients susceptible to malignant hyperthermia and in the management of malignant hyperthermia.
Effects of amlodipine on other medicinal products
Medicines with blood pressure-lowering effects
The blood pressure lowering effects of amlodipine adds to the blood pressure-lowering effects of other medicinal products with antihypertensive properties,
Atorvastatin, digoxin, warfarin, cyclosporin
In clinical interaction studies, amlodipine did not affect the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin, digoxin, warfarin or cyclosporin.
Simvastatin
Co-administration of multiple doses of 10mg of amlodipine with 80mg simvastatin resulted in a 77% increase in exposure to simvastatin compared to simvastatin alone. Limit the dose of simvastatin to 20mg daily in patients on amlodipine.
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
Pregnancy
Use in pregnancy is only recommended when there is no sager alternative and when the disease itself carries greater risk for the mother and foetus. The safety of amlodipine in human pregnancy has not been established. In animal studies, reproductive toxicity was observed at high doses.
Lactation
A dicision on whether to continue/discontinue breast-feeding or to continue/discontinue therapy with amlodipine should be made taking into account the benefit of breast-feeding to the child and the benefit of amlodipine therapy to the mother. It is not known whether amlodipine is excreted in breast milk.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
Hypertensive crisis
The safety and efficacy of amlodipine in hypertensive crisis has not been established.
Use in patients with cardiac failure
Patients with heart failure should be treated with caution. In a long-term, placebo controlled study in patients with severe heart failure (NYHA class Ⅲand Ⅳ) the reported incidence of pulmonary oedema was higher in the amlodipine treated group than in the placebo group. Calcium channel blockers, including amlodipine, should be used with caution in patients with congestive heart failure, as they may increase the risk of future cardiovascular events and mortality.
Use in patients with renal failure
Amlodipine may be used in such patients at normal doses. Changes in amlodipine plasma concentrations are not correlated with degree of renal impairment. Amlodipine is not dialyzable.
Use in patients with impaired hepatic function
The half life of amlodipine is prolonged and AUC values are higher in patients with impaired liver function; dosage recommendations have not been established. Amlodipine should therefore be initiated at the lower end of the dosing range and caution should be used, both on initial treatment and when increasing the dose. Slow dose titration and careful monitoring may be required in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Use in elderly patients
In the elderly increase of the dosage should take place with care.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Calcium channel blockers; selective calcium channel blockers with mainly vascular effects; dihydropyridines derivatives.
Mechanism of Action
Amlodipine is a calcium ion influx inhibitor of the dihydropyridine group (slow channel blocker or calcium ion antagonist) and inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into cardiac and vascular smooth muscle.
The mechanism of the antihypertensive action of amlodipine is due to a direct relaxant effect on vascular smooth muscle. The precise mechanism by which amlodipine relieves angina has not been fully determined but amlodipine reduces total ischaemic burden by the following two actions:
1. Amlodipine dilates peripheral arterioles and thus, reduces the total peripheral resistance (afterload) against which the heart works. Since the heart rate remains stable, this unloading of the heart reduces myocardial energy consumption and oxygen requirements.
2. The mechanism of action of amlodipine also probably involves dilatation of the main coronary arteries and coronary arterioles, both in normal and ischaemic regions. This dilatation increases myocardial oxygen delivery in patients with coronary artery spasm (Prinzmetal’s or variant angina).
In patients with hypertension, once daily dosing provides clinically significant reductions of blood pressure in both the supine and standing positions throughout the 24 hour interval. Due to the slow onset of action, acute hypotension is not a feature of amlodipine administration.
In patients with angina, once daily administration of amlodipine increases total exercise time, time to angina onset, and time to 1mm ST segment depression, and decreases both angina attach frequency and glyceryl trinitrate tablet consumption.
Amlodipine has not been associated with any adverse metabolic effects or changes in plasma lipids and is suitable for use in patients with asthma, diabetes, and gout.
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
