OMEZ Capsule
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
Dr. REDDY'S LABORATORIES LTD, India
ក្រុមហ៊ុនចែកចាយឱសថនៅប្រទេសកម្ពុជា:
DKSH


- សារធាតុសកម្ម
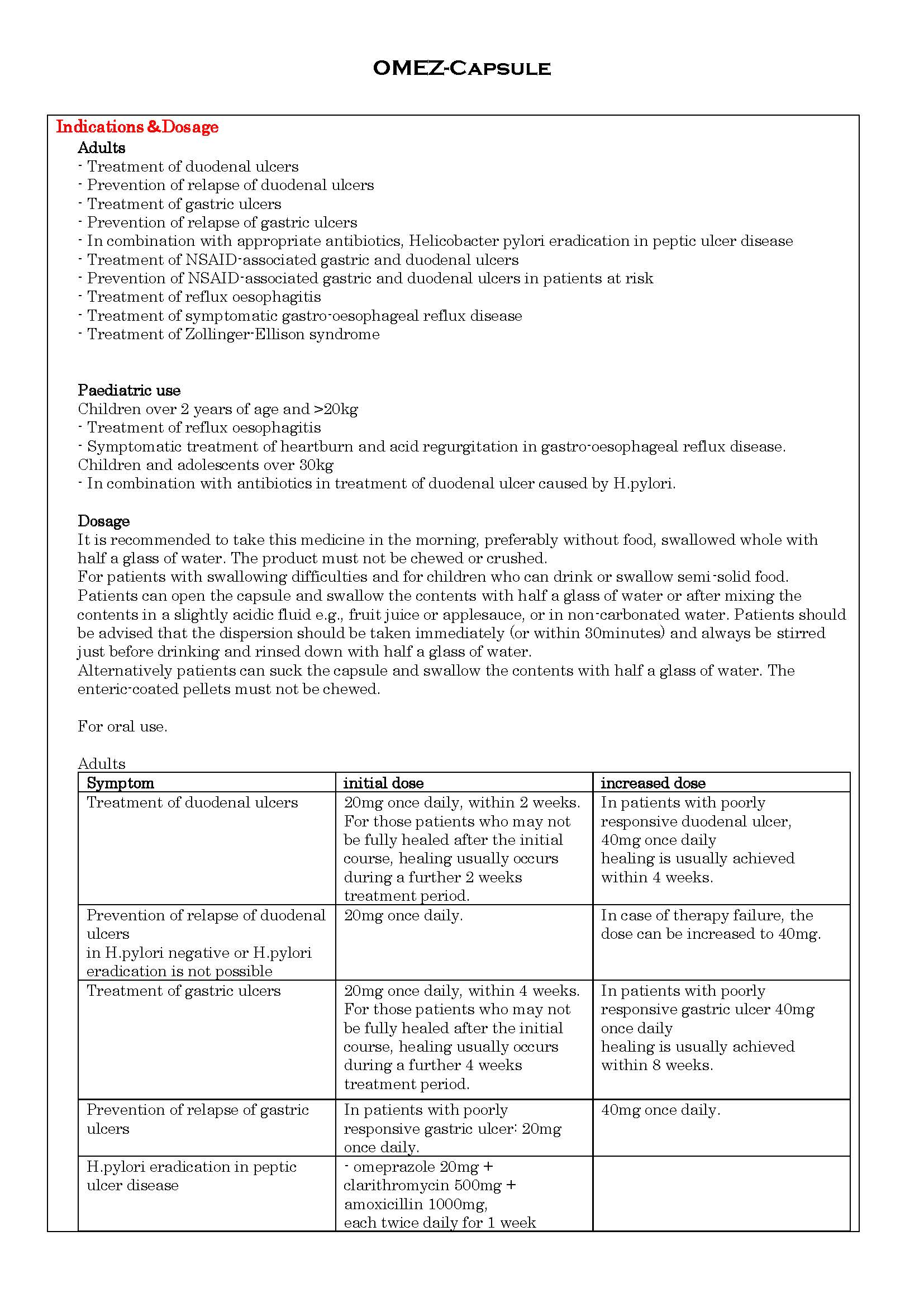
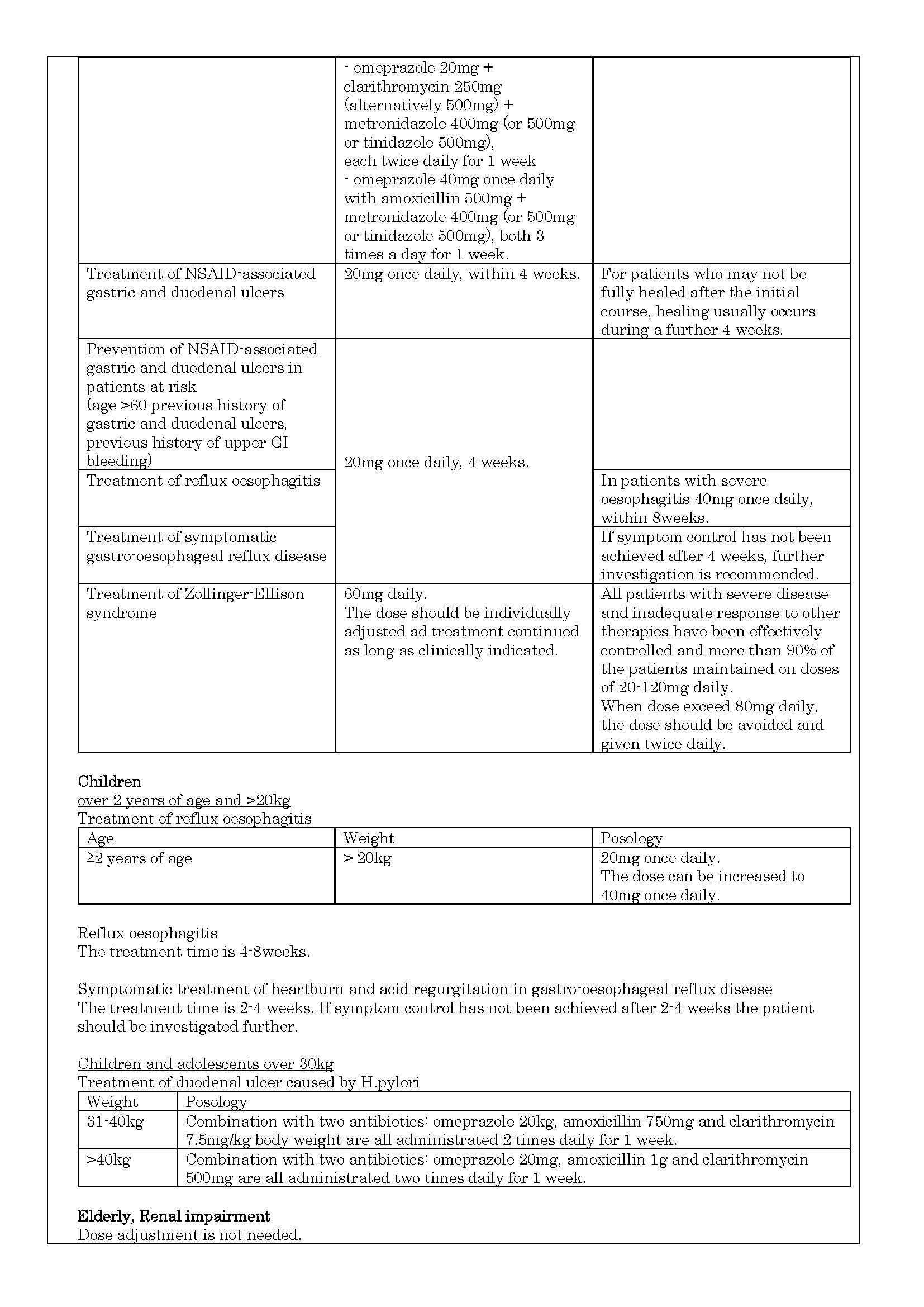
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
Omeprazole 20mg
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់

-
ហាមប្រើ
- hypersensitivity to omeprazole, substituted benzimidazoles or to any of the excipients,
- omeprazole like other PPIs must not be used concomitantly with nelfinavir.
-
ផលរំខាន
Side effects
The most common side effects (1-10% of patients) are headache, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhoea, flatulence, nausea/vomiting.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Rare: leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
Very rare: agranulocytosis, pancytopenia
Immune system disorders
Rare: hypersensitivity reactions e.g. fever, angioedema and anaphylactic reaction/shock
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Rare: hyponatraemia
Not known: hypomagnesaemia, severe hypomagnesaemia may result in hypocalcaemia. Hypomagnesaemia may also be associated with hypokalaemia.
Psychiatric disorders
Uncommon: insomnia
Rare: agitation, confusion, depression
Very rare: aggression, hallucination
Nervous system disorders
Common: headache
Uncommon: dizziness, paraesthesia, somnolence
Eye disorders
Rare: blurred vision
Ear and labyrinth disorders
Uncommon: vertigo
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Rare: bronchospasm
Gastrointestinal disorders
Common: abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhoea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting
Rare: dry mouth, stomatitis, gastrointestinal candidiasis
Not known: microscopic colitis
Hepatobiliary disorders
Uncommon: increased liver enzymes
Rare: hepatitis with or without jaundice
Very rare: hepatic failure, encephalopathy in patients with pre-existing liver disease
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Uncommon: dermatitis, pruritus, rash, urticaria
Rare: alopecia, photosensitivity
Very rare: erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Uncommon: hip fracture, wrist fracture, spinal fracture
Rare: arthralgia, myalgia
Very rare: muscular weakness
Renal and urinary disorders
Rare: interstitial nephritis
Reproductive system and breast disorders
Very rare: gynaecomastia
General disorders and administration site conditions
Uncommon: malaise, peripheral oedema
Rare: increased sweating
Paediatric population: See package insert.
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
Active substances with pH dependent absorption
The decreased intragastric acidity during treatment with omeprazole might increase or decrease the absorption of active substances with a gastric pH dependent absorption.
Nelfinavir, atazanavir, Digoxin, Clopidogrel, Posaconazole, erlotinib, ketoconazole, itraconazole
Active substances metabolized by CYP2C19
The metabolism of concomitant active substances also metabolized by CYP2C19 may be decreased and the systemic exposure to these substances increased.
Cilostazol, phenytoin,
Unknown mechanism
Saquinavir, Methotrexate, Tacrolimus
Inhibitors CYP2C19 and/or CYP34
Active substances known to inhibit CYP2C19 or CYP3A4 may lead to increased omeprazole serum levels by decreasing omeprazole’s rate of metabolism.
Clarithromycin, voriconazole
Induces of CYP2C19 and/or 3A4
Active substances known to induce CYP2C19 or CYP3A4 may lead to decreased omeprazole serum levels by increasing omeprazole’s rate of metabolism.
Rifampicin, St John’s wort
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
Pregnancy
Omeprazole can be used during pregnancy.
Lactation
Omeprazole is excreted in breast milk but is not likely to influence the child when therapeutic doses are used.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
Precautions
Gastric malignancy
In the presence of any alarm symptom (e.g. significant unintentional weight loss recurrent vomiting, dysphagia, haematemesis or melena) and when gastric ulcer is suspected or present, malignancy should be excluded, as treatment may alleviate symptoms and delay diagnosis.
Vitamin B12 absorption
Omeprazole may reduce the absorption of Vitamin B12 due to hypo- or achlorhydria. This should be considered in patients with reduced body stores or risk factors for reduced vitamin B12 absorption on long-term therapy.
Children with chronic illnesses
Some children with chronic illnesses may require long-term treatment although it is not recommended.
Risk of gastrointestinal infections
Treatment with PPI may lead to slightly increased risk of gastrointestinal infections such as Salmonella and Campylobacter. PPI therapy may also be associated with an increased risk of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea (CDAD). A diagnosis of CDAD should be considered for patients taking PPIs who develop diarrhoea that does not improve. Symptoms include watery stool, abdominal pain and fever, which may develop into more serious intestinal conditions. Factors that may predispose an individual to developing CDAD include advanced age, certain chronic medical conditions and taking broad spectrum antibiotics. Patients should use the lowest dose and shortest duration of PPI therapy appropriate to the condition being treated.
Risk of hip, wrist and spine fracture
PPIs, especially if used in high doses and over long durations (>1year), may modestly increase the risk of hip, wrist and spine fracture, predominantly in the elderly or in presence of other recognized risk factors.
Exceeding a treatment
When exceeding a treatment period of 1 year, patients should be kept under regular surveillance.
Hypomagnesaemia
For patients expected to be on prolonged treatment or who take PPIs with digoxin or drugs that may cause hypomagnesaemia (e.g., diuretics), health care professionals should consider measuring magnesium levels before starting PPI treatment and periodically during treatment.
Interference with laboratory tests
Increased chromogranin A (CgA) levels may interfere with investigations for neuroendocrine tumours. To avoid this interference the omeprazole treatment should be temporarily stopped 5 days before CgA measurements.
Sucrose, Lactose
capsules contain sucrose and lactose.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
Omeprazole, a racemic mixture of two enantiomers reduces gastric acid secretion through a highly targeted mechanism of action. It is a specific inhibitor of the acid pump in the parietal cell. It is rapidly acting and provides control through reversible inhibition of gastric acid secretion with once daily dosing.
Omeprazole is a weak base and is concentrated and converted to the active form in the highly acidic environment of the intracellular canaliculi within the parietal cell, where it inhibits the enzyme H+K+-ATPase- the acid pump. This effect on the final step of the gastric acid formation process is dose-dependent and provides for highly effective inhibition of both basal acid secretion and stimulated acid secretion, irrespective of stimulus.
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
