MOXIGET Tablet
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
Getz pharma, USA
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
Moxifloxacin 400mg
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
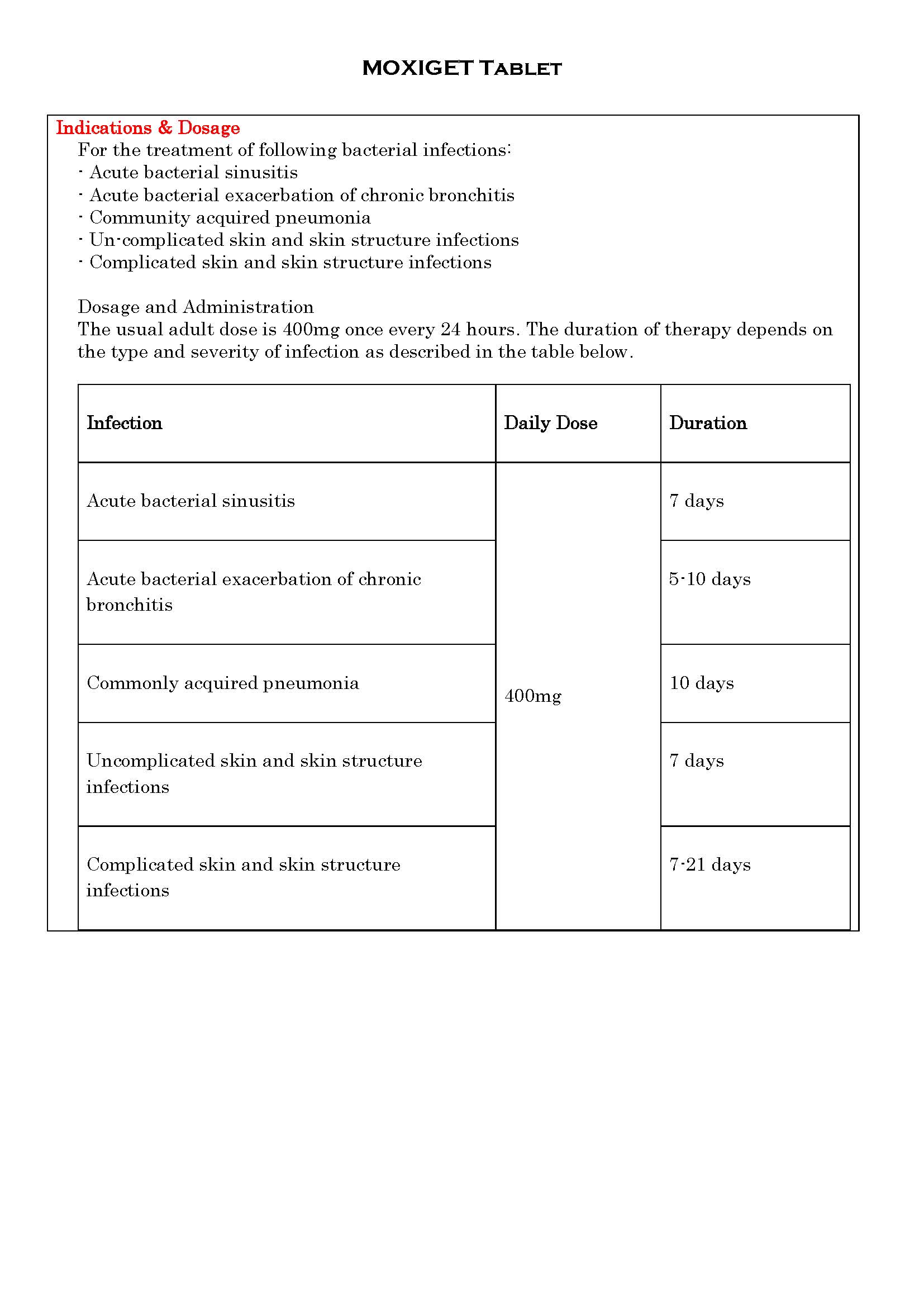
-
ហាមប្រើ
In patients:
- With hypersensitivity to moxifloxacin or other quinolones and any components if this medication.
- Less than 18 years of age.
- Pregnancy and lactation.
- With history of tendon disease/disorder related to quinolone treatment.
- With impaired liver function and in patients with transaminases >5 fold ULN.
- With congenital or documented acquired QT prolongation.
- With electrolyte disturbances, particularly in uncorrected hypokalaemia.
- With clinically relevant bradycardia.
- With clinically relevant heart failure with reduced left-ventricular ejection fraction.
- With previous history of symptomatic arrhythmias.
- Receiving Class ⅠA (e.g. quinidine, procainamide) or Class Ⅲ(amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents or other drugs that prolong the QT interval.
- With rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
-
ផលរំខាន
Most adverse reactions were mild to moderate.
The most common adverse reactions were nausea and diarrhea.
Common
Headache, dizziness, abdominal pain, vomiting, QT prolongation in patients with hypokalemia, increase in transaminases, superinfection due to resistant bacteria.
Uncommon
Anorexia, constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence, gastritis, increase amylase, QT prolongation, palpitations, tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, angina pectoris, dyspnea, hepatic impairment, increased bilirubin, increase gamma glutaryl transferase, increase in blood alkaline phosphatase, pruritis rash, urticaria, dry skin, arthralgia, myalgia, dehydration, visual disturbances, anxiety reactions, psychomotor hyperactivity, taste disorder, paresthesia/dysesthesia, confusion, disorientation, hyperlipidemia, allergic reaction, anaemia, leucopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia.
Rare
Dysphagia, pseudomembranous colitis, ventricular tachyarrhythmias, syncope, hypertension, hypotension, vasodilatation, tinnitus, hypoesthesia, smell disorder, abnormal dreams, disturbed coordination, seizures, disturbed attention, speech disorders, amnesia, anaphylaxis, allergic edema/angioedema, hyperglycaemia, hyperuricemia, emotional liability, depression, hallucination, prothrombin time prolonged.
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
See the package insert about the details below:
- antacids containing magnesium, calcium or aluminium, as well as sucralfate, metal cations such as iron, and multivitamin preparations with zinc or Didanosine.
- medication that can reduce potassium levels
- charcoal
- warfarin or its derivatives
- NSAIDs
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
Contraindicated.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
Warning
Fluoroquinolones, including moxifloxacin are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 50 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants.
Precautions
- As with all quinolones, moxifloxacin should be used with caution i patients with known or suspected CNS disorders or in the presence of other risk factors that may predispose to seizures or lower the threshold.
- Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents and may range in severity from mild to moderate to life threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhoea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents.
- Tendon inflammation and/or rupture have been reported with quinolone antibiotics. Risk may be increased with concurrent corticosteroids, particularly in the elderly. Discontinue at first signs or symptoms of tendon pain.
- Use with caution in diabetes as glucose regulation may be altered.
- Patients with a family history of, or actual glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency are prone to haemolytic reactions when treated with quinolones. Therefore, moxifloxacin should be used with caution in these patients.
- Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred with quinolone therapy. If an allergic reaction occurs discontinue drug immediately.
- Quinolones should be used with caution as they may exacerbate myasthenia gravis.
- Peripheral neuropathy may rarely occur.
- Elderly patients with renal disorders should use moxifloxacin with caution if they are unable to maintain adequate fluid intake, because dehydration may increase the risk of renal failure.
- Liver function tests/investigations should be performed in cases where indications of liver dysfunction occur.
- If vision becomes impaired or any effects on the eyes are experienced, an eye specialist should be consulted immediately.
- Moxifloxacin may result in an impairment of the patient’s ability to drive or operate machinery due to CNS reactions (e.g. dizziness; acute, transient loss of vision) or acute and short lasting loss of consciousness. Patients should be advised to see how they react to moxifloxacin before driving or operating machinery.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
Moxifloxacin is bactericidal against a range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. Such activity arises through the inhibition of DNA gyrase (topoisomeraseⅡ) and topoisomeraseⅣ, which bacteria require for DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination. Moxifloxacin contains the C8-methoxy moiety that augments its antibacterial activity and reduces the possibility of Gram-positive mutations. Because the 8-fluoroquinolones use a different mechanism of action than do the aminoglycosides, beta-lactams, macrolides, or tetracyclines, there has been no cross resistance between the quinolones and these antimicrobial agents.
Microbiology:
Aerobic Gram-positive micro-organisms:
Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible)
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus epidermidis (methicillin-susceptible)
Streptococcus anginosus
Aerobic Gram-negative micro-organisms:
Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Moraxella catarrhalis
Enterobacter cloacae
Escherichia coli
Proteus mirabilis
Anaerobic micro-organisms:
Fusobacterium species
Prevotella species
Peptostreptococcus species
Others:
Chlamydia pneumoniae
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Legionella pneumophila
Mycobacterium leprae
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
