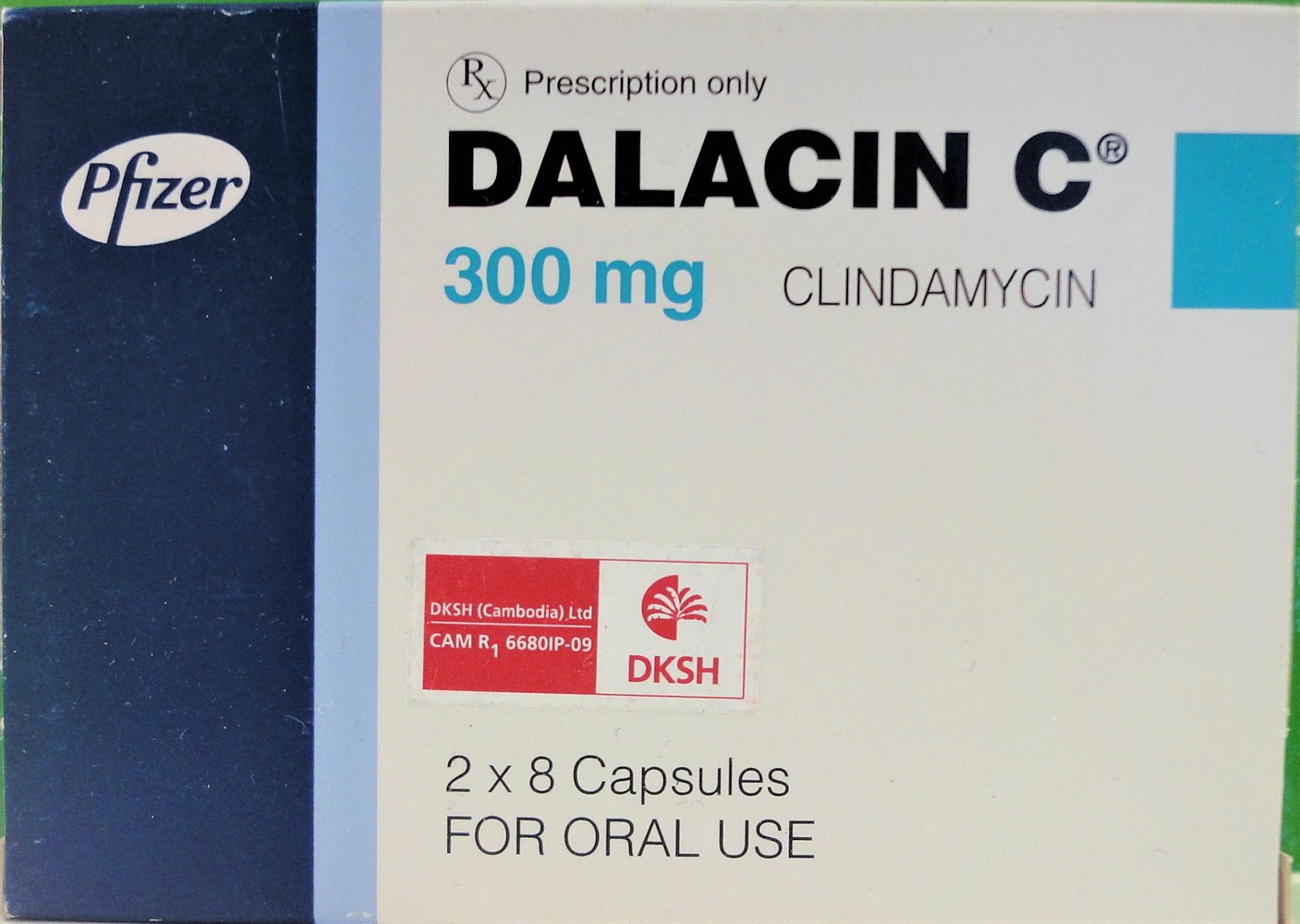
DALACIN C Capsule
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
Fareva Amboise-Zone Industrielle, France.
ក្រុមហ៊ុនចែកចាយឱសថនៅប្រទេសកម្ពុជា:
DKSH
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
គុណភាពព្យាបាល៖
ឱសថនេះប្រើសម្រាប់ព្យាបាលជំងឺច្រើនប្រភេទដូចជា៖
- ជំងឺផ្លូវដង្ហើមផ្នែកខាងលើដូចជា រលាកអាម៊ីដាល រលាកបំពង់ក រលាកឆ្អឹងរូងច្រមុះ រលាកក្នុងត្រចៀក ក្តៅខ្លួន
- ជំងឺផ្លូវដង្ហើមផ្នែកខាងក្រោមដូចជា រលាកទងសួត រលាកសួតរ៉ាំរ៉ៃ ហើមសួត និងអាប់សែសួត
- ជំងឺស្បែកនិងជាលិកាទន់ដូចជា មុនធំ ដំបៅងារ ឬរបួសក្លាយ ពងខ្ទុះ អាប់សែ
- ជំងឺឆ្អឹង និងសន្លាក់ឆ្អឹងដូចជា រលាកខួរឆ្អឹង និងសន្លាក់ឆ្អឹង
- ជំងឺរោគស្ត្រី ដូចជា រលាកស្បូន រលាកទ្វារមាស រលាកបំពង់អូវ៉ែរ រលាកដែស្បូន រលាកឆ្អឹងត្រគៀក រលាកកស្បូន
- ជំងឺក្នុងពោះដូចជា រលាកស្រោមពោះ អាប់សែពោះ
- ជំងឺផ្សេងៗដូចជារលាកបេះដូង អាប់សែធ្មេញ គ្រុនចាញ់ និងបង្ការការឆ្លងរោគក្នុងការវះកាត់ក និងក្បាល។
កម្រិត និងរបៀបប្រើ៖ ត្រូវអនុវត្តតាមវេជ្ជបញ្ជារបស់គ្រូពេទ្យព្យាបាល
- មនុស្សពេញវ័យ៖ លេប 2-6 គ្រាប់ (600-1800ម.ក្រ) ចែកជា 2 ឬ 3 ឬ 4 ដងក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ លេបជាមួយទឹកឱ្យបានគ្រប់គ្រាន់ជៀសវាងរលាកបំពង់ក។
- កុមារអាយុលើសពី 1ឆ្នាំ៖ លេប 8-25ម.ក្រ ក្នុងមួយគីឡូក្រាមនៃទម្ងន់ក្មេង ចែកជា 3 ឬ 4ដងក្នុង1ថ្ងៃ លេបជាមួយទឹកឱ្យបានគ្រប់គ្រាន់ជៀសវាងរលាកបំពង់ក។
*សំគាល់
ហាមប្រើឱសថនេះ ក្នុងការព្យាបាលជំងឺរលាកស្រោមខួរដោយឱសថនេះមិនអាចជ្រាបចូលក្នុងខួរក្បាល។
Clindamycin has been shown to be affective in the treatment of the following infections when caused by susceptible anaerobic bacteria: susceptible strains of gram-positive aerobic bacteria such as streptococci, staphylococci and pneumococci: and susceptible trains of Chlamydia trachomatis.
a) Upper respiratory infections including tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, otitis media and scarlet fever.
b) Lower respiratory infections including bronchitis, pneumonia, empyema and lung abcess.
c) Skin and soft tissue infections including acne, furuncles, cellulitis, impetigo, abscesses, and wound infections. For specific skin and soft tissue infections like erysipelas and paronychia (panaritium), it would seem logical that these conditions would respond very well to clindamycin therapy.
d) Bone and joint infections including osteomyelitis and septic arthritis.
e) Gynecological infections including endometritis, cellulitis, vaginal cuff infection and tubo-ovarian abscess, salpingitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease when given in conjunction with an antibiotic of appropriate gram-negative aerobic spectrum. It cases of cervicitis due to Chlamydia trachomatis, single drug therapy with clindamycin has been shown to be affective in eradicating the organism.
f) Intra-abdominal infections including peritonitis and abdominal abscess when given in conjunction with an antibiotic of appropriate gram-negative aerobic spectrum.
g) Septicemia and endocarditis - The effectiveness of clindamycin in the treatment of selected cases of endocarditis has been documented when clindamycin is determined to be bactericidal to the infecting organism by in vitro testing of appropriate achievable serum concentrations.
h) Dental infections such as periodontal abscess and periodontitis.
i) Toxoplasmic encephalitis in patients with AIDS. In patients who are intolerant to conventional treatment, clindamycin in combination with pyrimethamine has been shown to be efficacious.
j) Pneumocystis jiroveci (previously classified as Pneumocytis carinii) pneumonia in patients with AIDS. In patients who are intolerant to, or do not respond adequately to conventional treatment, clindamycin may be used in combination with primaquine.
k) Malaria, including multi-resistant Plasmodium falciparum, in combination with quinine.
l) Prophylaxis of endocarditis in patients sensitive/allergic to penicillin(s).
In vitro susceptibility to clindamycin has been shown for the following organisms: B.melaninogenicus, B.disiens, B.bivius, Peptostreptococcus spp., G.vaginalis, M.mulieris, M.curtisii, and Mycoplasma hominis.
Dosage
Adults
Clindamycin hydrochloride capsules (oral administration):
600-1800mg/day divided in 2,3 or 4 equal doses. To avoid the possibility of esophageal irritation, clindamycin HCl capsules should be taken with a full glass of water.
Dosage in Children (over 1month of age)
Clindamycin hydrochloride capsules (for children who are able to swallow capsules):
To avoid the possibility of esophageal irritation, clindamycin HCl capsules should be taken with a fll glass of water.
Doses of 8-25mg/kg/day in 3,4 equal doses.
Clindamycin capsules are not suitable for children who are unable to swallow them whole. The capsules do not provide exact mg/kg doses therefore it may be necessary to use the clindamycin palmitate oral solution in some cases.
See the package insert about the details below:
Dosage in Elderly
Dosage adjustments are not necessary in the elderly with normal hepatic function and normal (age-adjusted) renal function.
Dosage in Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Dosage modification is not necessary.
Dosage in Specific Indications
a) Treatment of Beta-Hemolytic Streptococcal Infections
b) Treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis Cervicitis
c) Treatment of Toxoplasmic Encephalitis in patients with AIDS
d) Treatment of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in patients with AIDS
e) Treatment of Acute Streptococcal Tonsillitis/Pharyngitis
f) Treatment of Malaria
g) Prophylaxis of Endocarditis in Patients Sensitive to Penicillin.
-
ហាមប្រើ
ចំពោះអ្នកធ្លាប់មានប្រតិកម្មជាមួយ Clindamycin ឬ Lincomycin ឬជាមួយសារធាតុផ្សំណាមួយនៃឱសថនេះ។
Contraindicated in patients previously found to be sensitive to clindamycin or lincomycin, or to any component of the formulation.
-
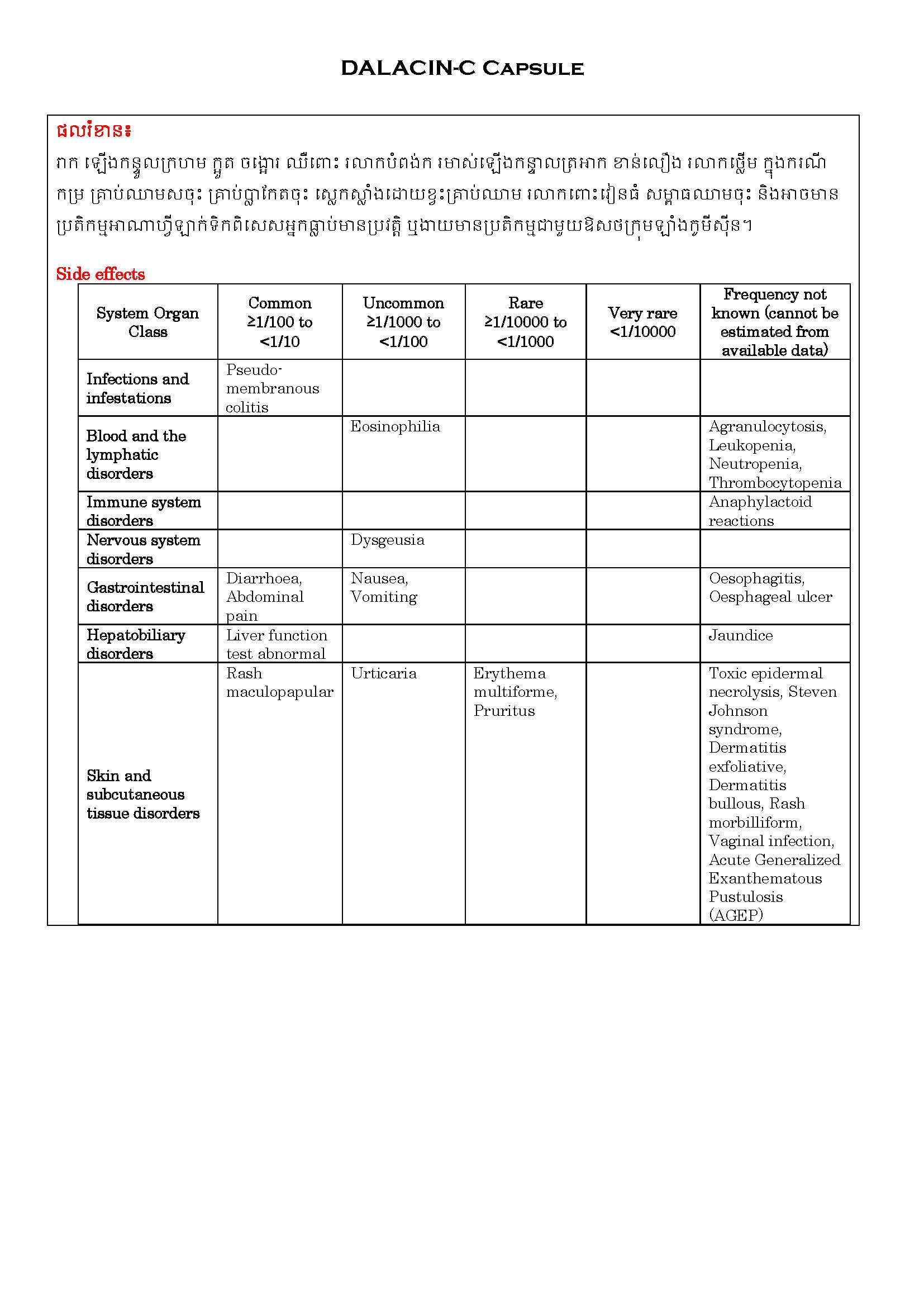
ផលរំខាន
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
អាចមានអន្តរកម្មជាមួយឱសថ Erythromycin, Neuromuscular agent។
See the package insert about the details below:
Neuromuscular blocking agents
Inhibitors of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5
Strong CYP3A4 inducers such as rifampicin
Clinically important interactions between clindamycin and co-administered drugs metabolized by CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2E1 and CYP2D6 are unlikely.
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ឱសថនេះគួរជៀសវាងប្រើចំពោះស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ ពិសេសក្នុងត្រីមាសទី1 លើកលែងតែមានការចាំបាច់ខ្លាំងព្រោះឱសថនេះអាចជ្រាបចូលក្នុងសុកទារក។
- ឱសថនេះអាចប្រើចំពោះស្ត្រីបំបៅកូនតែត្រូវផ្អាកការបំបៅដោះកូនជាបណ្តោះអាសន្ន ព្រោះឱសថនេះអាចជ្រាបចូលក្នុងទឹកដោះម្តាយ។
- Clindamycin អាចបង្កផលប៉ះពាល់ធ្ងន់ធ្ងរដល់ប្រព័ន្ធរំលាយអាហាររបស់ទារកដែលបៅដោះម្តាយ ដូចជាការរាករូស ឬឈាមនៅក្នុងលាមក ឬកន្ទួល។ ប្រសិនបើម្តាយដែលបំបៅកូនដោយទឹកដោះរបស់ខ្លួន ត្រូវការ Clindamycin តាមមាត់ ឬចាក់តាមសរសៃឈាម ដោយមិនចង់បញ្ឈប់ការបំបៅកូនដោយទឹកដោះរបស់ខ្លួននោះ គេអាចប្រើឱសថផ្សេងទៀតជំនួសបាន។ អត្ថប្រយោជន៍នៃការលូតលាស់ និងសុខភាពពីការបំបៅកូនដោយទឹកដោះ ត្រូវបានគិតគូររួមជាមួយតម្រូវការព្យាបាលម្តាយសម្រាប់ធាតុផ្សំ Clindamycin និងផលប៉ះពាល់អវិជ្ជមានណាមួយមកពីធាតុផ្សំ Clindamycin លើកុមារដែលបំបៅទឹកដោះ ម្តាយ ឬមកពីស្ថានភាពរបស់ម្តាយ។
See the package insert about the details:
Pregnancy
Clindamycin should be used in pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
If oral clindamycin is required by a nursing mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding, but an alternate drug may be preferred. The developmental and health benefits breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for clindamycin and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from clindamycin or from the underlying maternal condition.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- ការប្រើឱសថនេះរយៈពេលយូរអាចបង្កើតនូវមេរោគថ្មី (ជំងឺថ្មី) ដែលស៊ាំនឹងឱសថនេះហេតុនេះប្រសិនបើមានត្រូវឈប់ប្រើ និងរកការព្យាបាលជាបន្ទាន់។
- ការប្រើឱសថនេះរយៈពេលយូរអាចធ្វើឱ្យមានការរាករូសរ៉ាំរ៉ៃ (Psudomembraneous colitis) ដែលត្រូវព្យាបាលជាបន្ទាន់។
- ត្រូវប្រើឱសថនេះដោយប្រុងប្រយ័តចំពោះអ្នកជំងឺថ្លើម (ខាន់លឿង) អ្នកខ្សោយតម្រងនោម និងត្រូវធ្វើការត្រួតពិនិត្យមុខងារថ្លើម និងតម្រងនោមក្នុងករណីប្រើរយៈពេលយូរ។
- ឱសថនេះគួរជៀសវាងប្រើចំពោះស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ ពិសេសក្នុងត្រីមាសទី1 លើកលែងតែមានការចាំបាច់ខ្លាំងព្រោះឱសថនេះអាចជ្រាបចូលក្នុងសុកទារក។
- ឱសថនេះអាចប្រើចំពោះស្ត្រីបំបៅកូនតែត្រូវផ្អាកការបំបៅដោះកូនជាបណ្តោះអាសន្ន ព្រោះឱសថនេះអាចជ្រាបចូលក្នុងទឹកដោះម្តាយ។
- Clindamycin អាចបង្កផលប៉ះពាល់ធ្ងន់ធ្ងរដល់ប្រព័ន្ធរំលាយអាហាររបស់ទារកដែលបៅដោះម្តាយ ដូចជាការរាករូស ឬឈាមនៅក្នុងលាមក ឬកន្ទួល។ ប្រសិនបើម្តាយដែលបំបៅកូនដោយទឹកដោះរបស់ខ្លួន ត្រូវការ Clindamycin តាមមាត់ ឬចាក់តាមសរសៃឈាម ដោយមិនចង់បញ្ឈប់ការបំបៅកូនដោយទឹកដោះរបស់ខ្លួននោះ គេអាចប្រើឱសថផ្សេងទៀតជំនួសបាន។ អត្ថប្រយោជន៍នៃការលូតលាស់ និងសុខភាពពីការបំបៅកូនដោយទឹកដោះ ត្រូវបានគិតគូររួមជាមួយតម្រូវការព្យាបាលម្តាយសម្រាប់ធាតុផ្សំ Clindamycin និងផលប៉ះពាល់អវិជ្ជមានណាមួយមកពីធាតុផ្សំ Clindamycin លើកុមារដែលបំបៅទឹកដោះ ម្តាយ ឬមកពីស្ថានភាពរបស់ម្តាយ។
- ឱសថនេះមិនប៉ះពាល់ដល់សមត្ថភាពបើកបរ ឬបញ្ជាម៉ាស៊ីនទេ តែបើមានផលរំខានត្រូវផ្អាកសិន។
Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including severe skin reactions such as drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis have been reported in patients receiving clindamycin therapy. If a hypersensitivity or severe skin reaction occurs, clindamycin should be discontinued and appropriate therapy should be initiated.
Pseudomembraneous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including clindamycin, and may range in severity form mild to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider the diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents.
Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is a primary cause of “antibiotic-associated colitis”. After the primary diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, therapeutic measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to drug discontinuation alone. In moderate-to –severe cases, consideration should be given to management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation, and treatment with an antibacterial drug clinically effective against Clostridium difficile colitis.
Since clindamycin does not diffuse adequately into cerebrospinal fluid, the drug should not be used in the treatment of meningitis.
If therapy is prolonged, liver and kidney function tests should be performed.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including clindamycin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C difficile.
C.difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C.difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
ជាអង់ទីប៊ីយ៉ូទិកស្ថិតក្នុងក្រុម Lincomycin មានមុខងារប្រឆាំងនឹងមេរោគ Gram + ច្រើនប្រភេទដែលអាចរស់នៅដោយមិនត្រូវការខ្យល់។
Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. It binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit and affects both ribosome assembly and the translation process. Although clindamycin phosphate is inactive in vitro, rapid in vivo hydrolysis converts this compound to the antibacterially active clindamycin. At usual doses, clindamycin exhibits bacteriostatic activity in vitro.
Antimicrobial activity
Clindamycin has been shown to have in vitro activity against most isolates of the following organisms:
Aerobic bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates)
Coagulase-negative staphylococci (methicillin-susceptible isolates)
Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptive isolates)
Beta-hemolytic streptococci groups A,B,C, and G
Viridans group streptococci
Corynebacterium spp.
Gram-negative bacteria
Chlamydia tachomatis
Anaerobic bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
Actinomyces spp.
Clostridium spp. (expect Clostridium difficile)
Eggerthella (Eubacterium) spp.
Peptococcus spp.
Peptostreptococcus spp. (Finegoldia magna, Micromonas micros)
Propionibacterium acnes
Gram-negative bacteria
Bacteriodes spp.
Fusobaterium spp.
Gardnerella vaginalis
Prevotella spp.
Fungi
Pneumocystis jiroveci
Protozoans
Toxoplasma gondii
Plasmodium falciparum
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
