CRAVIT Tablet
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
INTERTHAI PNARMACEUTICAL MANUFACTURING LTD., Thailand
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
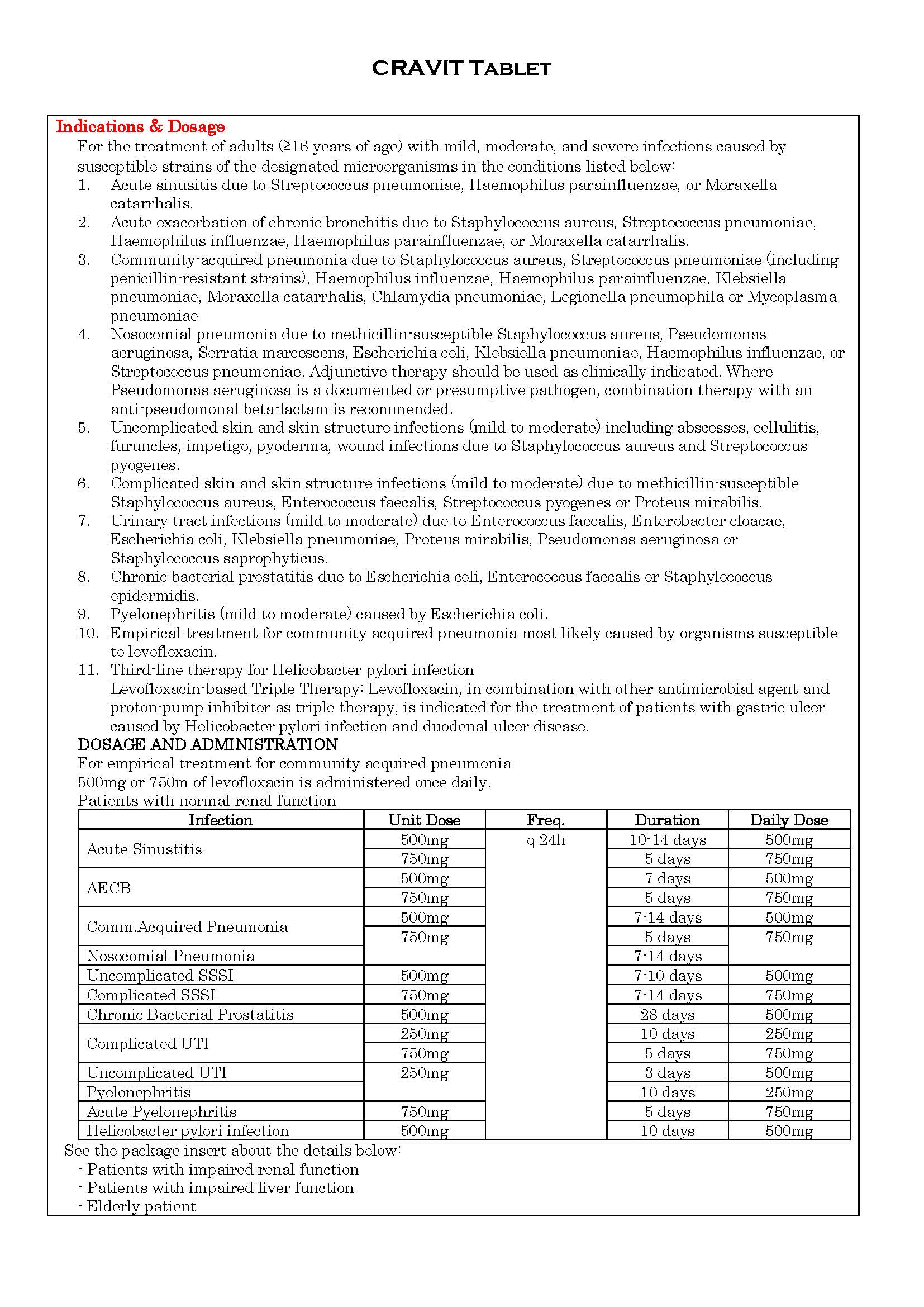
-
ហាមប្រើ
1. Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to levofloxacin, ofloxacin or any excipients of this product
2. Patients with epilepsy
3. Patients with history of tendon disorder related to fluoroquinolones administration
4. Children or adolescents below the age of 16 years
5. Pregnant women or women suspected of being pregnant
6. Breast-feeding women
-
ផលរំខាន
・Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Uncommon: anemia
Very rare: thrombocytopenia*
Unknown: pancytopenia*, agranulocytosis*, hemolytic anemia with hemoglobinuria*
・Immune system disorder
Unknown: anaphylactoid reaction*
・Metabolism and nutrition disorder
Uncommon: anorexia
Unknown: hypoglycemia (hypoglycaemic coma may occur)*, hyperglycemia
・Psychiatric disorders
Common: sleep loss
Unknown: psychiatric symptoms such as confusion*, delirium*, depression*, hallucination
・Nervous system disorders
Common: dizziness, headache
Uncommon: somnolence, numbness, tremor, mental dullness, dysgeusia
Rare: consciousness disturbed
Very rare: convulsion*, ageusia
Unknown: peripheral nerve disorder, extrapyramidal disorder, anosmia, parosmia
・Eye disorders
Rare: abnormal vision
・Ear and labyrinth disorders
Uncommon: tinnitus
Unknown: hearing losses
・Cardiac disorders
Uncommon: palpitations
Unknown: ventricular tachycardia (including Torsades de pointes)*, QT prolonged*, tachycardia
・Vascular disorders
Very rare: shock*
Unknown: hypotension
・Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Uncommon: dry throat
Unknown: interstitial pneumonia*, eosinophilic pneumonia*
・Gastrointestinal disorders
Common: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort
Uncommon: abdominal pain dyspepsia, abdominal distension, constipation
Rare: stomatitis
Very rare: glossitis
Unknown: colitis with bloody stool, such as pseudomembranous colitis*
・Hepatobiliary disorders
Uncommon: hepatic function abnormal
Unknown: hepatitis fulminant*, Jaundice*
・Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Uncommon: pruritus, rash
Rare: hyperhidrosis. urticaria
Very rare: photosensitivity
Unknown: toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)*, Oculomucocutaneous syndrome (Stevens-Johnson syndrome)*, hypersensitivity vasculitis*
・Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Uncommon: arthralgia, pain in extremity, back pain, weakness
Rare: arthropathy, myalgia
Unknown: rhabdomyolysis*, tendon disorders such as Achilles tendonitis or tendon rupture*, exacerbation of myasthenia gravis*, muscle rupture
・Renal and urinary disorders
Uncommon: hematuria
Rare: pollakisuria, oliguria, acute renal failure*
Unknown: interstitial nephritis*, anuria, dysuria, urinary retention
General disorders and administration site conditions
Uncommon: thirst, chest discomfort, malaise, feeling hot, edema
Very rare: pyrexia
Unknown: chest pain
Investigations
Common: AST increased, ALT increased, LDH increased, white blood cell count decreased, eosinophil count increased
Uncommon: creatinine increased, urinary protein positive, alkaline phosphatase increased, gamma-GTP increased, blood bilirubin increased, lymphocyte count decreased, neutrophil count decreased, CPK increased, glucose urine present, blood glucose decreased, platelet count decreased
Rare: BUN increased, urine output decreased
Very rare: blood glucose increased
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
See the package insert about the details below:
1. Antacid, Sucralfate, Metal Cations, Multivitamins
2. Theophylline, Fenbufen, or similar NSAIDs (phenylacetic acid/propionic acid derivatives)
3. Antidiabetic agents
4. Anticoagulant drug (warfarin and its derivatives)
5. ClassⅠA antiarrhythmics and ClassⅢantiarrhythmics
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
See the package insert about the details:
Contraindicated
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
This tablet should be administered with caution in the following patients:
1. Patients with impaired renal function
2. Patients exposed to direct sunlight
3. Patients with known or suspected CNS disorder that may predispose to seizures or lower the seizure threshold
4. Diabetic patients receiving concomitant treatment with an oral hypoglycemic agent (especially, sulfonylureas or with insulin preparations)
5. Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to quinolone antibiotics
6. Patients with serious heart diseases e.g. arrhythmia and ischemic heart disease. [QT prolonged may occur] patients with uncorrected electrolyte imbalance (e.g. hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia) and patients receiving Class ⅠA and Ⅲantiarrhythmic agents
7. Patients with myasthenia gravis [symptoms may be exacerbated]
WARNINGS
1. Levofloxacin is more soluble than other quinolones, adequate hydration of patients receiving levofloxacin should be maintained to prevent the formation of highly concentrated urine.
2. Acute renal failure or interstitial nephritis
3. Excessive exposure to sunlight should be avoided. However, phototoxicity has been observed very rare; incidence <0.01%. Therapy should be discontinued if phototoxicity (e.g. a skin eruption) occurs.
4. Dysglycemia: During post-marketing surveillance, hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia have been reported in patients taking levofloxacin. Serious symptoms such as hypoglycemic coma have been reported in patients receiving levofloxacin. Hypoglycemia may be prone to develop in patients with diabetes mellitus (especially, those receiving sulfonylureas or insulin preparations), patients with impaired renal function and elderly patients.
5. Serious colitis with bloody stool, such as pseudomembranous colitis
6. Rhabdomyolysis characterized by myalgia. weakness, elevated CK(PCK) and increased myoglobin in plasma and urine, etc., and accompanied with acute exacerbation of renal function
7. Tendon disorder such as Achilles tendonitis or tendon rupture: If symptoms such as pain and edema in the peritendinous region are observed, treatment with levofloxacin should be discontinued immediately and appropriate therapeutic measures taken. The risk of tendonitis and tendon rupture is increased in those over age 60, in those on concomitant corticosteroid therapy, and transplant recipients.
8. Levofloxacin may inhibit the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and therefore, may give false-negative results in the bacteriological diagnosis of tuberculosis.
9. Some undesirable effects may impair the patient’s ability to concentration and react and therefore may constitute a risk in situation where these abilities are of special importance (e.g. driving a car or operating machinery).
10. Shock or anaphylactoid reaction (initial symptoms: erythema, rigor, dyspnea, etc)
11. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) or Oculomucocutaneous syndrome (Stevens-Johnson syndrome)
12. Convulsion
13. QT prolonged and ventricular tachycardia (including Torsades de pointes): During post-marketing surveillance, prolonged QT which may sometimes lead to the occurrence of ventricular tachycardia including torsades de pointes have been reported spontaneously in patients taking levofloxacin. The risk of the events may be increased in patients with serious heart diseases (e.g. arrhythmia and ischemic heart disease), patients with uncorrected hypokalemia, patents receiving ClassⅠA (quinidine sulfate, procainamide hydrochloride) and ClassⅢ(amiodarone hydrochloride, sotalol hydrochloride) antiarrhythmic agents and in elderly patients
14. Hepatitis fulminant, hepatic function disorder or jaundice (initial symptoms: nausea, vomiting, anorexia, malaise, pruritus, etc.)
15. Pancytopenia, agranulocytosis (initial symptoms: pyrexia, pharynx pain, malaise, etc.), hemolytic anemia with hemoglobinuria or thrombocytopenia
16. Interstitial pneumonia or eosinophilic pneumonia accompanied with pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, abnormal chest X-ray, or eosinophilia, etc.
17. Psychiatric symptoms such as confusion,, delirium and depression.
18. Hypersensitivity vasculitis: If symptoms such as pyrexia, abdominal pain, arthralgia, purpura or maculopapules, and skin biopsy evidence of leukocytoclastic vasculitis are observed, treatment with levofloxacin should be discontinued immediately and appropriate therapeutic measures taken.
19. Exacerbation of myasthenia gravis.
20. Patients received Levofloxacin dose of 750mg may develop some adverse reaction such as dizziness, headache, nausea or vomiting more than Levofloxacin dose of 500mg.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
Levofloxacin is the -isomer of the racemate, ofloxacin, a quinolone antimicrobial agent. The antibacterial activity of ofloxacin resides primarily in the L-isomer. It is two folds stronger than that of ofloxacin.
The mechanism of action of levofloxacin and other fluoroquinolone antimicrobials involve inhibition of bacterial topoisomeraseⅣand DNA gyrase (both of which are typeⅡtopoisomerases), enzymes required for DNA replication, transcription, repair and recombination.
Levofloxacin has in vitro activity against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. Levofloxacin is often bactericidal at concentrations equal to or slightly greater than inhibitory concentrations.
Fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin, differ in chemical structure and mode of action from aminoglycosides, macrolides and beta-lactam antibiotics, including penicillins. Fluoroquinolones may, therefore, be active against bacteria resistant to these antimicrobials.
Resistance to levofloxacin due to spontaneous mutation in vitro is a rare occurrence. Although cross-resistance has been observed between levofloxacin and some other fluoroquinolones, some microorganisms resistant to other fluoroquinolones may be susceptible to levofloxacin.
Levofloxacin has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section:
Aerobic gram-positive microorganisms
Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Streptococcus pneumoniae (including penicillin-resistant strains), Streptococcus pyogenes
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms
Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, Moraxella catarrhalis, Proteus mirabillis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Other microorganisms
Chlamydia pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown.
Aerobic gram-positive microorganisms
Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus (Group C/F), Streptococcus (Group G), Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus milleri, Viridans group streptococci
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms
Acinetobacter baumannii, Acinetobacter lwoffii, Bordetella pertussis, Citrobacter (diversus) koseri, Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterobacter sakazakii, Klebsiella oxytoca, Morganella morganii, Pantoea (Enterobacter) agglomerans, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia rettgeri, Providencia stuartii, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Serratia marcescens
Anaerobic gram-positive microorganisms
Clostridium perfringens
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
