AZIF Capsule
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
FREDUN PARMACEUTICALS LTD., India
ក្រុមហ៊ុនចែកចាយឱសថនៅប្រទេសកម្ពុជា:
KOU HUN CHEA IMPORT EXPORT CO. LTD.
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
Azithromycin 250mg
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
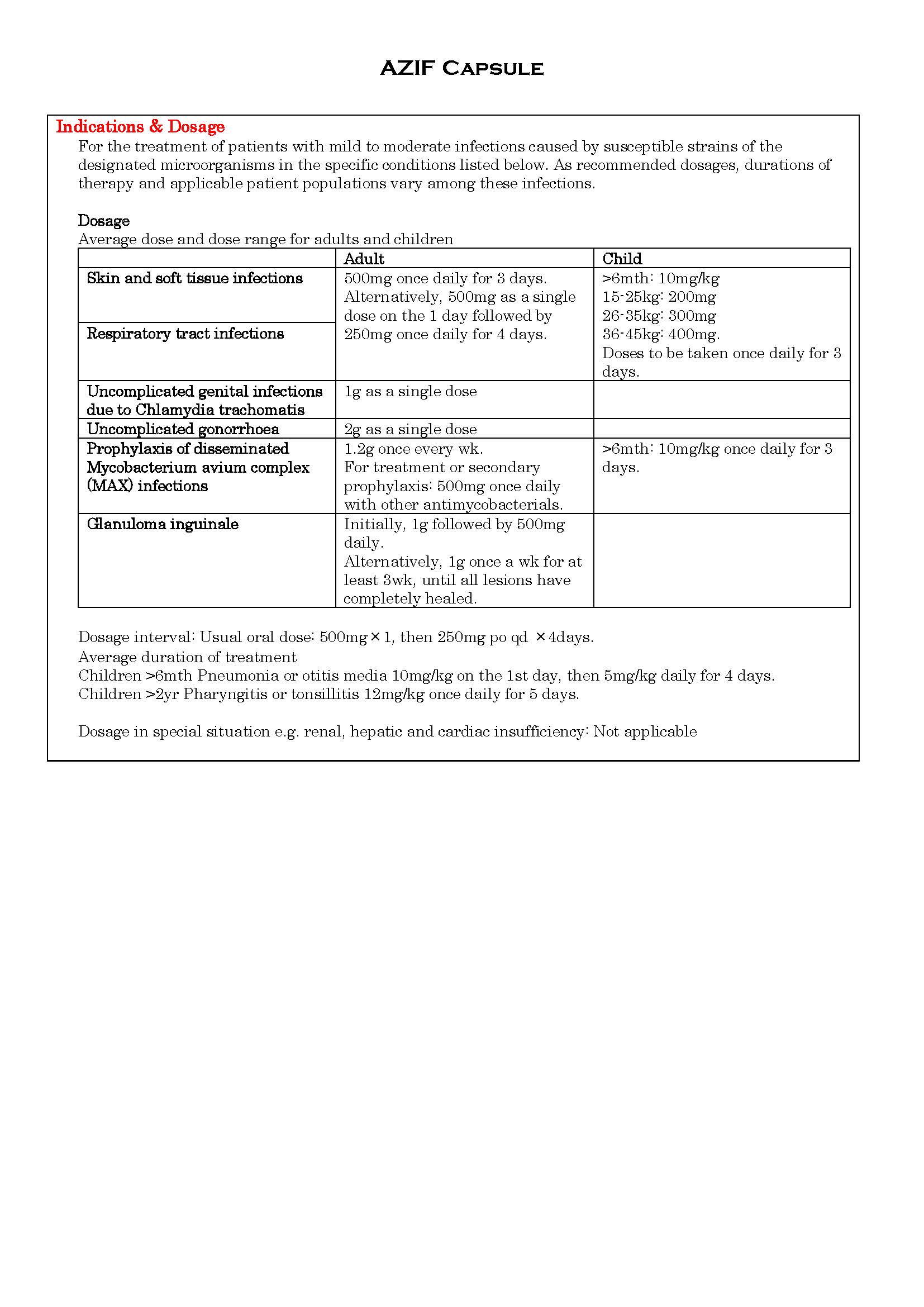
-
ហាមប្រើ
In patients with known hypersensitivity to Azithromycin, erythromycin, any macrolide or ketolide antibiotic.
-
ផលរំខាន
Mild to moderate nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, flatulence, diarrhoea, cramping, angioedema, cholestatic jaundice, dizziness, headache, vertigo, somnolence, transient elevations of liver enzyme values.
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
Aluminum- and magnesium-containing antacids, digoxin, live vaccines, lovastatin, nelfinavir, warfarin. This medication may decrease the effectiveness of combination-type birth control pills. This can result in pregnancy. You may need to use an additional form of reliable birth control of while using this medication.
Other drugs besides azithromycin which may affect the heart rhythm (QTc prolongation in the EKG) include dofetilide, pimozide, procainamide, quinidine, sotalol, and sparfloxacin among others. QTc prolongation can infrequently result in serious, rarely fatal, irregular heartbeats. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for details. Ask for instructions about whether you need to stop any other QTc-prolonging drugs you may be using in order to minimize the risk of this effect. Do not start or stop any medicine without doctor or pharmacist approval.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
Azithromycin is principally eliminated via the liver, caution should be exercised when Azithromycin is administered to patients with impaired hepatic function. Due to the limited data in subjects with GFR<10mL/min, caution should be exercised when prescribing Azithromycin in these patients.
Prolonged cardiac repolarization and QT interval, imparting a risk of developing cardiac arrhythmia and torsades de pointes, have been seen in treatment with other macrolides. A similar effect with Azithromycin cannot be completely ruled out in patients at increased risk for prolonged cardiac repolarization.
Exacerbation of symptoms of myasthenia gravis and new onset of myasthenic syndrome have been reported in patients receiving Azithromycin therapy.
Prescribing Azithromycin in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Warnings
Serious allergic reactions, including angioedema, anaphylaxis, and dermatologic reactions including Stevens Johnson Syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported rarely in patients on Azithromycin therapy. Although rare, fatalities have been reported. Despite initially successful symptomatic treatment of the allergic symptoms, when symptomatic therapy was discontinued, the allergic symptoms recurred soon thereafter in some patients without further Azithromycin exposure. These patients required prolonged period of observation and symptomatic treatment. This relationship of these episodes to the long tissue half-life of Azithromycin and subsequent prolonged exposure to antigen is unknown at present.
If an allergic reaction occurs, the drug should be discontinued and appropriate therapy should be instituted. Physicians should be aware that reappearance of the allergic symptoms may occur when symptomatic therapy is discontinued.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
Azithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic of the azalide subclass, exerts its antibacterial action by binding to the 50s ribosomal subunits of susceptible bacteria and suppressing protein synthesis.
Following oral administration, azithromycin is rapidly absorbed and distributed widely throughout the body. Rapid movement of azithromycin from blood into tissue results in significantly higher azithromycin concentrations in tissue than in plasma). The absolute bioavailability is approximately 37%.
Mechanism of action: Azithromycin blocks transpeptidation by binding to 50s ribosomal subunit of susceptible organisms and disrupting RNA-dependent protein synthesis at the chain elongation step.
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
