TENORMIN Injection
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
Astra Zeneca UK Limited,
United Kingdom
ក្រុមហ៊ុនចែកចាយឱសថនៅប្រទេសកម្ពុជា:
DKSH
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
Atenolol 5mg/10mL
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
i. Hypertension
ii. Angina pectoris
iii. Cardiac arrhythmias
iv. Myocardial infarction. Early and late intervention.
Posology and method administration
The dose must always be adjusted to individual requirements of the patients, with the lowest possible starting dosage. The following are guidelines.
Adults
Hypertension
1 tablet daily. Most patients respond to 100mg daily given orally as a single dose. Some patients, however, will respond to 50mg given as a single daily dose. The effect will be fully established after 1-2 weeks. A further reduction in blood pressure may be achieved by combining Tenormin with other antihypertensive agents. For example, co-administration of Tenormin with a diuretic, provides a highly effective and convenient antihypertensive therapy.
Angina
Most patients with angina pectoris will respond to 100mg given orally once or 50mg given twice daily. It is unlikely that additional benefit will be gained by increasing the dose.
Cardiac Arrhythmias
A suitable initial dose is 2.5mg injected intravenously over a 2.5 minute period (i.e. 1mg/min). This may be repeated at 5 minute intervals until a response is observed, up to a maximum dosage of 10mg.If Tenormin is given by infusion, 0.15mg/kg bodyweight may be administered over a 20minute period. If required, the injection or infusion may be repeated every 12 hours. Having controlled the arrhythmias with intravenous Tenormin, a suitable oral maintenance dosage is 50-100mg daily, given as a single dose.
Myocardial Infarction
Early intervention after acute myocardial infarction: For patients suitable for treatment with intravenous beta-blockade and presenting within 12 hours of the onset of chest pain. Tenormin 5-10mg should be given by slow intravenous injection (1mg/min) followed by Tenormin 50mg orally about 15 minutes later. provided no untoward effects have occurred from the intravenous dose. This should be followed by the further 50mg orally 12 hours after the intravenous dose and then 12 hours later by 100mg orally, once daily. If bradycardia and/or hypotension requiring treatment, or any other untoward effects occur, Tenormin should be discontinued.
Late intervention after acute myocardial infarction: For patients who present some days after suffering an acute myocardial infarction an oral dose of Tenormin (100mg daily) is recommended for long-term prophylaxis of myocardial infarction.
Elderly
Dosage requirements may be reduced, especially in patients with impaired renal function.
Children
There is no paediatric experience with Tenormin and for this reason it is not recommended for use in children.
Renal Failure
Since Tenormin is excreted via the kidneys the dosage should be reduced in cases of severe impairment of renal function.
No significant accumulation of Tenormin occurs in patients who have a creatinine clearance greater than 35ml/min/1.73m2 (normal range is 100-150ml/min/1.73m2).
For patients with a creatinine clearance of 15-35ml/min/1.73m2 (equivalent to serum creatinine of 300-600micromol/L) the oral dose should be 50mg daily and the intravenous dose should be 10mg once every 2 days.
For patients with a creatinine clearance of <15ml/min/1,73m2 (equivalent to serum creatinine of >600micromol/L) the oral dose should be 25mg daily or 50mg on alternate days and the intravenous dose should be 10mgonce every 4days.
Patients on haemodialysis should be given 50mg orally after each dialysis; this should be done under hospital supervision as marked falls in blood pressure can occur.
-
ហាមប្រើ
- known hypersensitivity to the active substance or any of the excipients
- bradycardia
- cardiogenic shock
- hypotension
- metabolic acidosis
- severe peripheral arterial circulatory disturbances
- second or third degree heart block
- sick sinus syndrome
- untreated phaechromocytoma
- uncontrolled heart failure.
-
ផលរំខាន
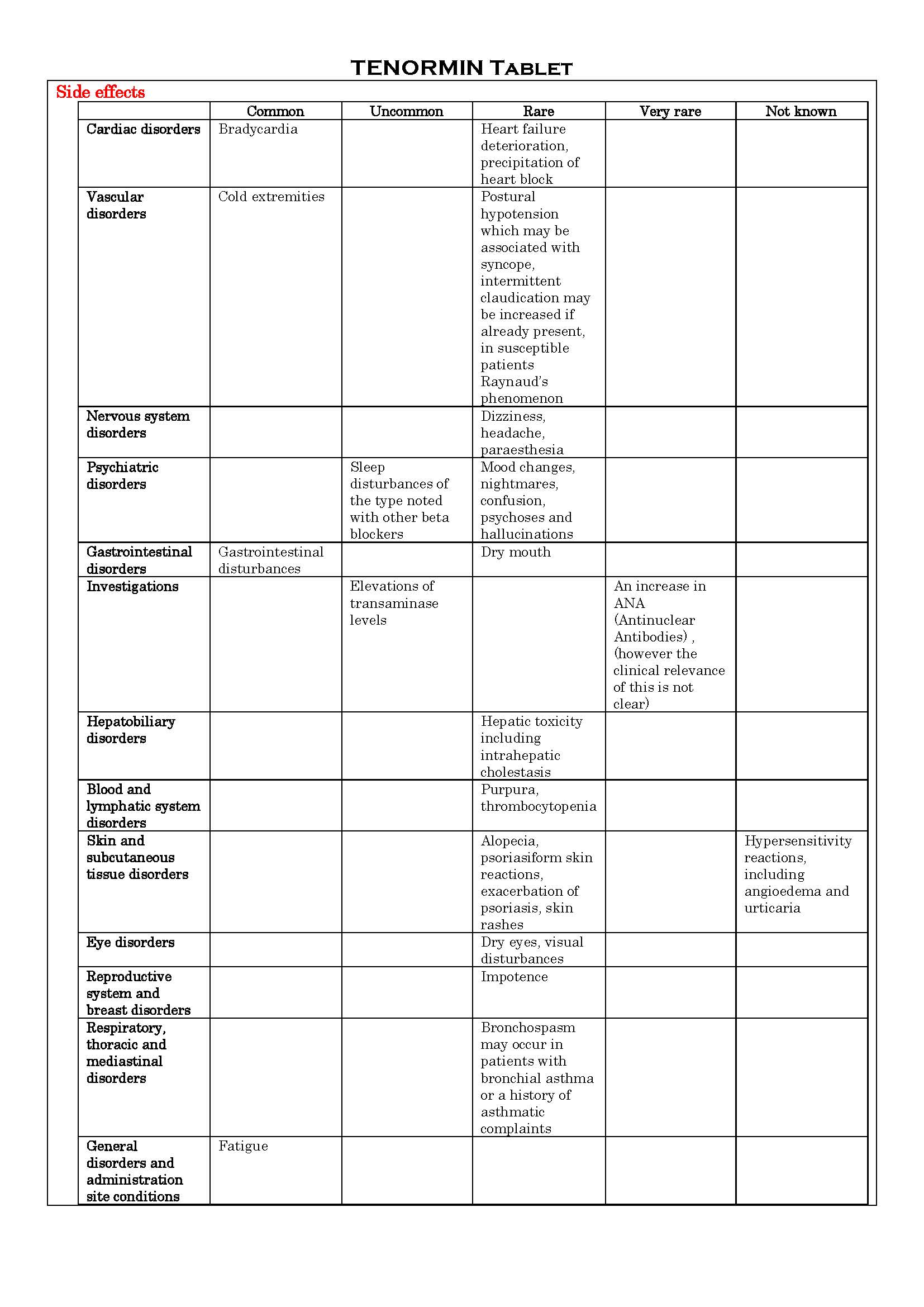
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
(see the package insert about details)
- calcium channel blockers with negative inotropic effects e.g. verapamil, diltiazem
- dihydropyridines e.g. nifedipine
- digitalis glycosides
- clonidine
- classⅠanti-arrhythmic drugs (e.g. disopyramide) and amiodarone
- sympathomimetic agents (e.g. adrenaline)
- insulin and oral antidiabetic drugs
- prostaglandin synthetase inhibiting drugs (e.g. ibuprofen, indomethacin)
- anaesthetic agents
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
Tenormin crosses the placental barrier and appears in the cord blood. No studies have been performed on the use of Tenormin in the first trimester and the possibility of foetal injury cannot be excluded. Tenormin has been used under close supervision for the treatment of hypertension in the third trimester. Administration of Tenormin to pregnant women in the management of mild to moderate hypertension has been associated with intra-uterine growth retardation.
The use of Tenormin in women who are, or may become, pregnant requires that the anticipated benefit be weighed against the possible risks, particularly in the first and second trimesters, since beta-blockers, in general, have been associated with a decrease in placental perfusion which may result in intra-uterine deaths, immature and premature deliveries.
There is significant accumulation of Tenormin in breast milk.
Neonates born to mothers who are receiving Tenormin at parturition or breast-feeding may be at risk of hypoglycaemia and bradycardia.
Caution should be exercised when Tenormin is administered during pregnancy or to a woman who is breast-feeding.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- should not be withdrawn abruptly. The dosage should be withdrawn gradually over a period of 7-14 days, to facilitate a reduction in beta-blocker dosage. Patients should be followed during withdrawal, especially those with ischaemic heart disease.
- when a patient is scheduled for surgery, and a decision is made to discontinue beta-blocker therapy, this should be done at least 24 hours prior to the procedure. The risk-benefit assessment of stopping beta-blockade should be made for each patient. If treatment is continued, an anaesthetic with little negative inotropic activity should be selected to minimize the risk of myocardial depression. The patient may be protected against vagal reactions by intravenous administration of atropine.
- although contraindicated in uncontrolled heart failure, may be used in patients whose signs of heart failure have been controlled. Caution must be exercised in patients whose cardiac reserve is poor.
- may increase the number and duration of angina attacks in patients with Prinzmetal’s angina due to unopposed alpha-receptor mediated coronary artery vasoconstriction. Tenormin is a beta1-selective beta-blocker; consequently, its use may be considered although utmost caution must be exercised.
- although contraindicated in severe peripheral arterial circulatory disturbances, may also aggravate less severe peripheral arterial circulatory disturbances.
- due to its negative effort on conduction time, caution must be exercised if it is given to patients with first degree heart block.
- may mask the symptoms of hypoglycaemia in particular tachycardia.
- may mask the signs of thyrotoxicosis.
- will reduce heart rate, as a result of its pharmacological action. In the rare instances when a treated patient develops symptoms which may be attributable to a slow heart rate and the pulse rate drops to less than 50-55bpm at rest, the dose should be reduced.
- may cause a more severe reaction to a variety of allergens, when given to patients with a history of anaphylactic reaction to such allergens. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of adrenaline used to treat the allergic reactions.
- may cause a hypersensitivity reaction including angioedema and urticaria.
- should be used with caution in the elderly, starting with a lesser dose.
Since Tenormin is excreted via the kidneys, dosage should be reduced in patients with a creatinine clearance of below 35ml/min/1.73m2.
Although cardioselective (beta1) beta-blockers may have less effect on lung function than non-selective beta-blockers, as with all, beta-blockers, these should be avoided in patients with reversible obstructive airways disease, unless there are compelling clinical reasons for their use. Where such reasons exist, Tenormin may be used with caution. Occasionally, some increase in airways resistance may occur in asthmatic patients, however, and this may usually be reversed by commonly used dosage of bronchodilators such as salbutamol or isoprenaline.
As with other beta-blockers, in patients with phaeochromocytoma, an alpha-blocker should be given concomitantly.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
(see the package insert about details.)
Betablocking agents, plain selective.
Atenolol is a beta-blocker which is beta-1-selective (i.e. acts preferentially on beta1-adrenergic receptors in the heart). Selectivity decreases with increasing dose.
Atenolol is without intrinsic sympathomimetic and membrane stabilizing activities and as with other beta-blockers, has negative inotropic effects (and is therefore contraindicated in uncontrolled heart failure).
The mode of action of atenolol in the treatment of hypertension is unclear.
It is probably the action of atenolol in reducing cardiac rate and contractility which makes it effective in eliminating or reducing the symptoms of patients with angina.
It is unlikely that any additional ancillary properties possessed by S(-) atenolol, in comparison with the racemic mixture, will give rise to different therapeutic effects.
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
