AZTHICOR Tablet
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
Salud Care (Ⅰ) Pvt .Ltd., India
ក្រុមហ៊ុនចែកចាយឱសថនៅប្រទេសកម្ពុជា:
GATES MEDICAL PLUS Co., Ltd
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
For the following bacterial infections induced by micro-organisms susceptible to azithromycin.
- Acute bacterial sinusitis (adequately diagnosed)
- Acute bacterial otitis media (adequately diagnosed)
- Pharyngitis, tonsillitis
- Acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis (adequately diagnosed)
- Mild to moderately severe community acquired pneumonia
- Infections of the skin and tissues of mild to moderate severity e.g. folliculitis, cellulitis, erysipelas
- Uncomplicated Chlamydia trachomatis urethritis and cervicitis
Consideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents.
Dosage
Azithromycin should be given as a single daily dose. Duration of the treatment for the different infection diseases is given below.
The tablets can be taken with or without food.
The tablets should be taken with 1/2 glass of water.
Children and adolescents with a body weight above 45kg, adults and elderly:
The total dose is 1500mg, administered as 500mg once daily for 3 days.
Alternatively, the same total dose (1500mg can be administered in a period of 5 days, 500mg on the first day and 250mg on day 2-5.
In the case of uncomplicated Chlamydia trachomatis urethritis and cervicitis, the dosage is 1000mg as a single dose.
Children and adolescents with a body weight below 45kg:
Azithromycin tablets are not suitable for patients under 45kg body weight. Other dosage forms are available for this group of patients.
For elderly patients the same dose as for adults can be acquired. Since elderly patients can be patients with ongoing proarrhythmic conditions a particular caution is recommended due to the risk of developing cardiac arrhythmia and torsades de pointes.
Patents with renal/hepatic impairment:
Dose adjustment is not required for patients with mild to moderate renal/hepatic impairment (GFR 10-80mL/min).
Mode of Administration
Azithromycin should be given as a single daily dose. Duration of the treatment for the different infection diseases is given below.
The tablets can be taken with or without food.
The tablets should be taken with 1/2 glass of water.
-
ហាមប្រើ
In patients with hypersensitivity to azithromycin, erythromycin, any macrolide or ketolide antibiotic, or to any of the excipient listed in section.
-
ផលរំខាន
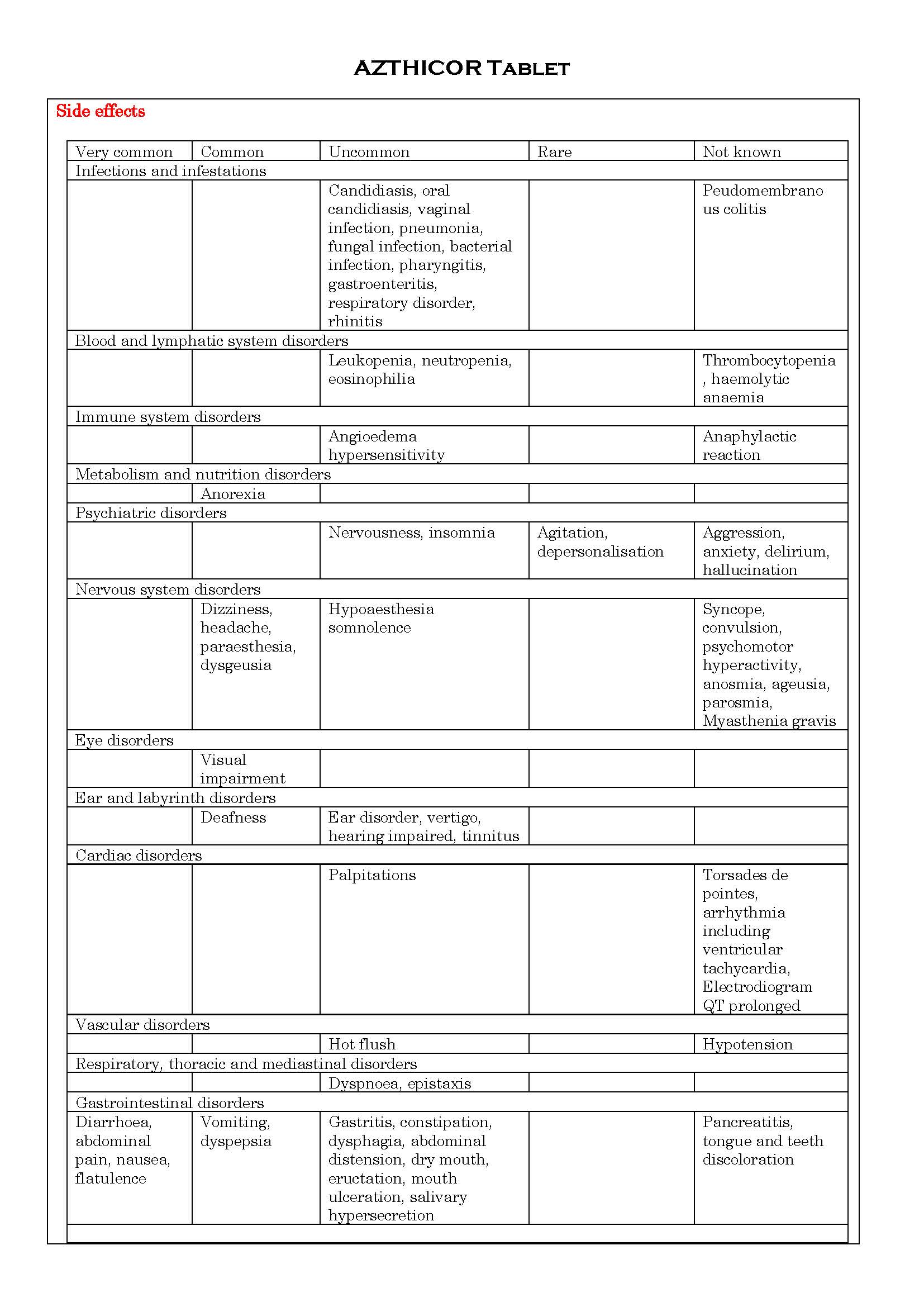
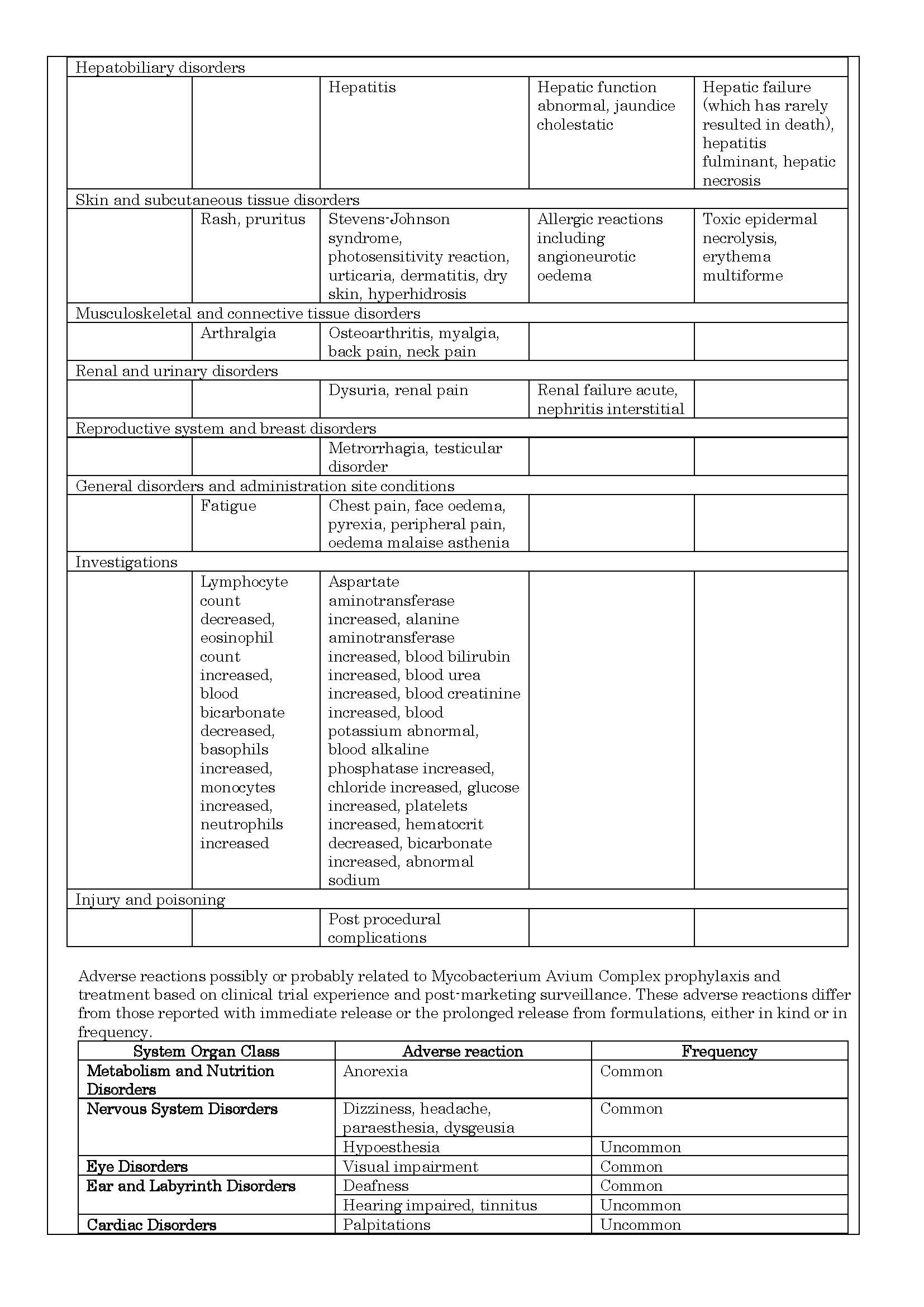
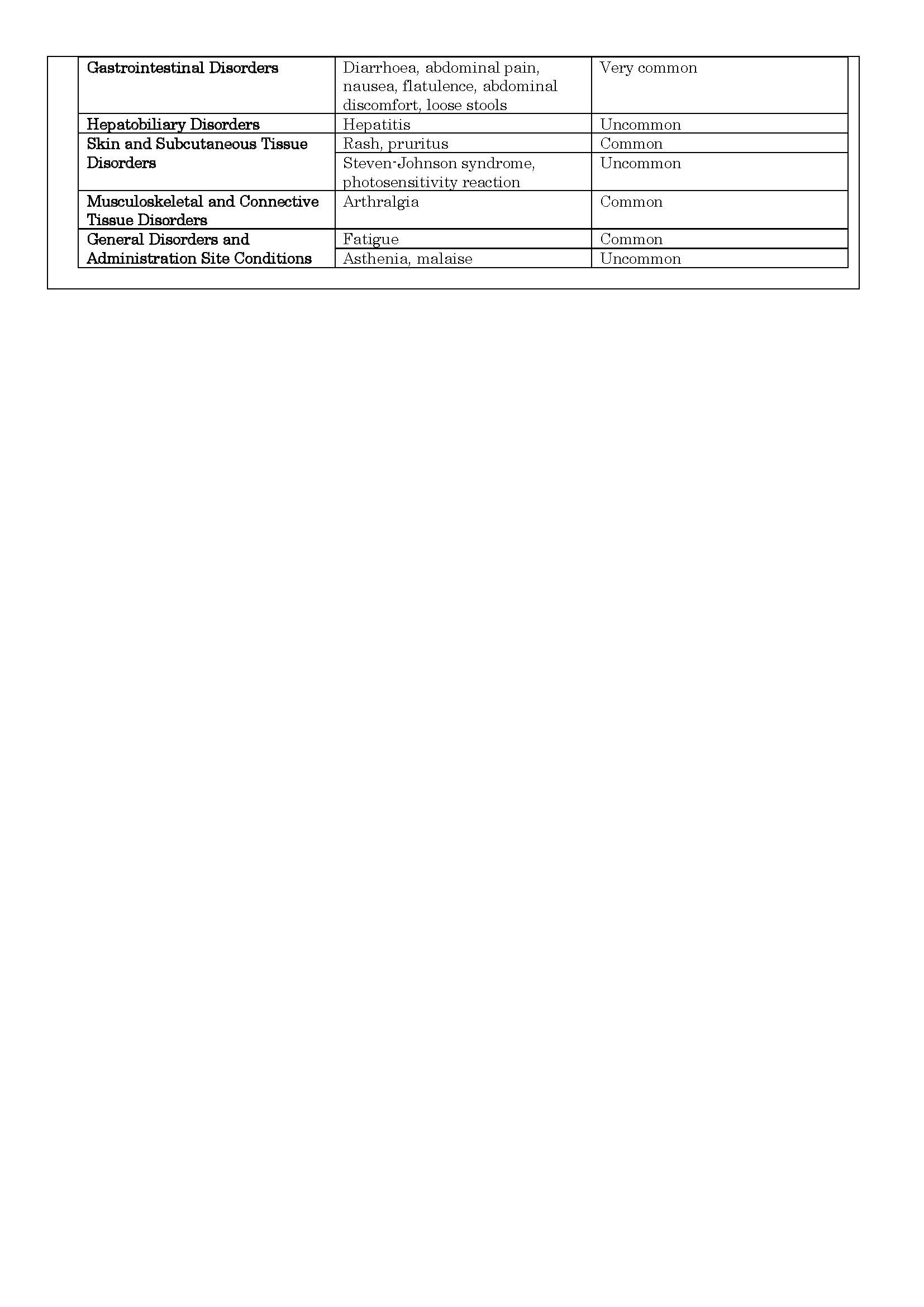
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
See the package insert about the details below:
Antacids
Cetirizine
Digoxin (P-gp substrates)
Zidovudine
Ergotamine derivatives
Astemizole, alfentanil
Carbamazepine
Cisapride
Cimetidine
Coumarin-Type Oral Anticoagulants
Cyclosporin
Efavirenz
Fluconazole
Indinavir
Methylprednisolone
Midazolam
Nelfinavir
Rifabutin
Sildenafil
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
(See the package insert about the details below.)
Pregnancy
Azithromycin should only be used during pregnancy if the benefit outweighs the risk.
Breast-feeding
It is recommended to discard the mild during treatment and up till 2 days after discontinuation of treatment. Nursing may be resumed thereafter.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
As with erythromycin and other macrolides, rare serious allergic reactions including angioneurotic oedema and anaphylaxis (rarely fatal), have been reported. Some of these reactions with azithromycin have resulted in recurrent symptoms and required a longer period of observation and treatment.
Since the liver is the principal route of elimination for azithromycin, the use of azithromycin should be undertaken with caution in patients with significant hepatic disease. Cases of fulminant hepatitis potentially leading to life-threatening liver failure have been reported with azithromycin. Some patients may have had pre-existing hepatic disease or may have been taking other hepatotoxic medicinal products.
In case of signs and symptoms of liver dysfunction, such as rapid developing asthenia associated with jaundice, dark urine, bleeding tendency or hepatic encephalopathy, liver function tests/investigations should be performed immediately. Azithromycin administration should be stopped if liver dysfunction has emerged.
In patients receiving ergot derivatives, ergotism has been precipitated by coadministration of some macrolide antibiotics. There are no data concerning the possibility of an interaction between ergotamine derivatives and azithromycin. However, because of the theoretical possibility of ergotism, azithromycin and ergot derivatives should not be co-administered.
Superinfections:
As with any antibiotic preparation, it is recommended to pay attention to signs of superinfection with non-suitable micro-organisms like fungi. A superinfection may require an interruption of the azithromycin treatment and initiation of adequate measures.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhoea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including azithromycin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhoea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C.difficile.
C.difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C.difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhoea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over 2 months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
In patients with severe renal impairment (GFR<10mL/min) a 33% increase in systemic exposure to azithromycin was observed.
Prolonged cardiac repolarisation and QT interval, impairing risk of developing cardiac arrhythmia and torsades de pointes, have been seen in treatment with other macrolides, including azithromycin. Therefore as the following situations may lead to an increased risk for ventricular arrhythmias (including torsade de pointes) which can lead to cardiac arrest, azithromycin should be used with caution in patients with ongoing proarrhythmic conditions (especially women and elderly patients) such as patients:
- With congenital or documented acquired QT prolongation.
- Currently receiving treatment with other active substances known to prolong QT interval such as antiarrhythmics of classⅠA (quinidine and procainamide) and classⅡ(dofetilide, amiodarone and sotalol), cisapride and terfenadine; antipsychotic agents such as pimozide; antidepressants such as citalopram; and fluoroquinolones such as moxifloxacin and levofloxacin.
- With electrolyte disturbance, particularly in cases of hypokalaemia and hypomagnesaemia
- With clinically relevant bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmia or severe cardiac insufficiency.
Exacerbations of the symptoms of myasthenia gravis and new onset of myasthenia syndrome have been reported in patients receiving azithromycin therapy.
Safety and efficacy for the prevention or treatment of Mycobacterium Avium Complex (MAC) in children have not been established.
The following should be considered before prescribing azithromycin:
Azithromycin is not suitable for treatment of severe infections where a high concentration of the antibiotic in the blood is rapidly needed.
The selection of azithromycin to treat an individual patient should take into account the appropriateness of using a macrolide antibacterial agent based on adequate diagnosis to ascertain the bacterial etiology of the infection in the approved indications and the prevalence of resistance to azithromycin or other macrolides. In areas with a high incidence of erythromycin A resistance, it is especially important to take into consideration the evolution of the pattern of susceptibility to azithromycin and other antibiotics.
As for other macrolides, high resistance rates of Streptococcus pneumoniae have been reported for azithromycin in some European countries. This should be taken into account when treating infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae.
In bacterial pharyngitis the use of azithromycin is recommended only in cases where first line therapy with beta-lactam is not possible.
Skin and soft tissue infections
The main causative agent of soft issue infections, Staphylococcus aureus, is frequently resistant to azithromycin. Therefore, susceptibility testing is considered a precondition for treatment of soft tissue infections with azithromycin.
Infected burn wounds:
Azithromycin is not indicated for the treatment of infected burn wounds.
Sexually transmitted disease:
In case of sexually transmitted diseases a concomitant infection by T.pallidium should be excluded.
Neurological or psychiatric diseases:
Azithromycin should be used with caution in patients with neurological or psychiatric disorders.
Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ

*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
