UTIL Capsule
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
AMBROSIA PHARMACEUTICALS, Pakistan
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
Esomeprazole 40mg
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
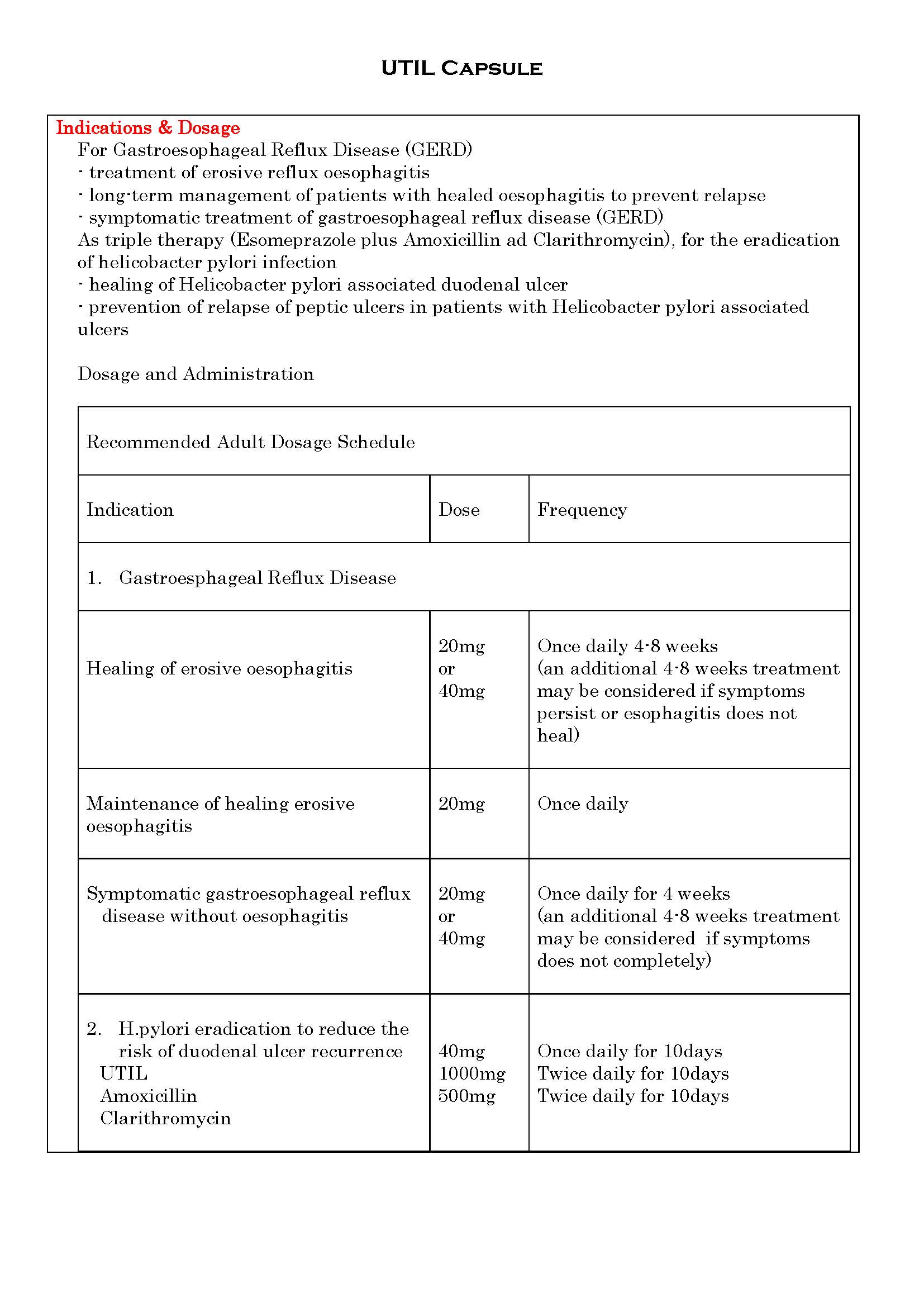
-
ហាមប្រើ
Known hypersensitivity to Esomeprazole, substituted benzimidazoles or any of the excipients.
-
ផលរំខាន
Uncommon
Peripheral oedema, Insomnia, Dizziness, Paraesthesia, Somnolence, Vertigo, Dry mouth, Increased liver enzymes, Dermatitis, Pruritus, Rash, Urticaria
Common
Headache Abdominal pain, Constipation, Diarrhoea, Flatulence, Nausea/Vomiting.
Rare
Leukopenia, Thrombocytopenia, Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. Fever, Angioedema and Anaphylactic reactions/shock), Hyponatraemia, Agitation, Confusion, Depression, Taste disturbance, Blurred vision, Bronchospasm, Stomatitis, Gastrointestinal candidiasis, Alopecia, Photosensitivity, Arthralgia, Myalgia, Increased sweating.
Very rare
Agranulocytosis, Pancytopenia, Aggression, Hallucinations, Hepatic failure, Encephalopathy in patients with pre-existing liver disease, Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), Muscular weakness, Interstitial nephritis.
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
Concomitant use of atazanavir and nelfinavir with proton pump inhibitors is not recommended.
Esomeprazole may potentially interfere with CYP2C19, the major Esomeprazole metabolizing enzyme. Co-administration of Esomeprazole 20mg and diazepam, a CYP2C19 substrate, resulted in a 45% decrease in clearance of diazepam. Avoid concomitant administration of Esomeprazole with clopidogrel. When using Esomeprazole, consider use of alternative anti-platelet therapy.
Drug-induced decrease in gastric acidity results in enterochromaffin-like cell hyperplasia and increased Chromogranin A levels which may interfere with investigations for neuroendocrine tumors.
Co-administration of Esomeprazole, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin has resulted in increases in the plasma levels of Esomeprazole and 14-hydroxyclarithromycin.
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
Pregnancy
For Esomeprazole, clinical data on exposed pregnancies are insufficient.
Lactation
Esomeprazole is likely present in human milk. Esomeprazole is the S-isomer of omeprazole and limited data indicate that maternal doses of Esomeprazole 20mg daily produce low levels in human milk. Caution should be exercised when Util is administered to a nursing woman.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
In the presence of any alarm symptom (e.g. significant unintentional weight loss, recurrent vomiting, dysphagia, haematemesis or melaena) and when gastric ulcer is suspected or present, malignancy should be excluded, as treatment with Util may alleviate symptoms and delay diagnosis. Patients on long-term treatment (particularly those treated for more than a year) should be kept under regular surveillance. Patients on on-demand treatment should be instructed to contact their physician if their symptoms change in character. When prescribing Esomeprazole for on demand therapy, the implications for interactions with other pharmaceuticals, due to fluctuating plasma concentrations of Esomeprazole should be considered. When prescribing Esomeprazole for eradication of Helicobacter pylori possible active substance interactions of all components in the triple therapy should be considered. Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption or sucrose-isomaltase insufficiency should not take this medicine.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
Esomeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor that suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the H+/K+-ATPase in the gastric parietal cell. The S- and R-isomers of omeprazole are protonated and converted in the acidic compartment of the parietal cell forming the active inhibitor, the chiral sulphonamide. By acting specifically on the proton pump, esomeprazole blocks the final step in acid production, thus reducing gastric acidity. This effect is dose-related up to a daily dose of 20mg to 40mg and leads to inhibition of gastric acid secretion.
PHARACOKINETICS
Esomeprazole is a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion and is indicated in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), the healing of erosive esophagitis, and H-pylori eradication to reduce the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence. Esomeprazole belongs to a new class of antisecretory compounds, the substituted benzimidazoles, that do not exhibit anticholinergic or H2 histamine antagonistic properties, but that suppress gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the H+/K+-ATPase at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell. By doing so, it inhibits acid secretion into the gastric lumen. This effect is dose-related and leads to inhibition of both basal and stimulated acid secretion irrespective of the stimulus.
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
