CEDIN-300 Capsule
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
SANCE LABORATORIES PRIVATE LIMITED, India
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
Cefdinir 300mg
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
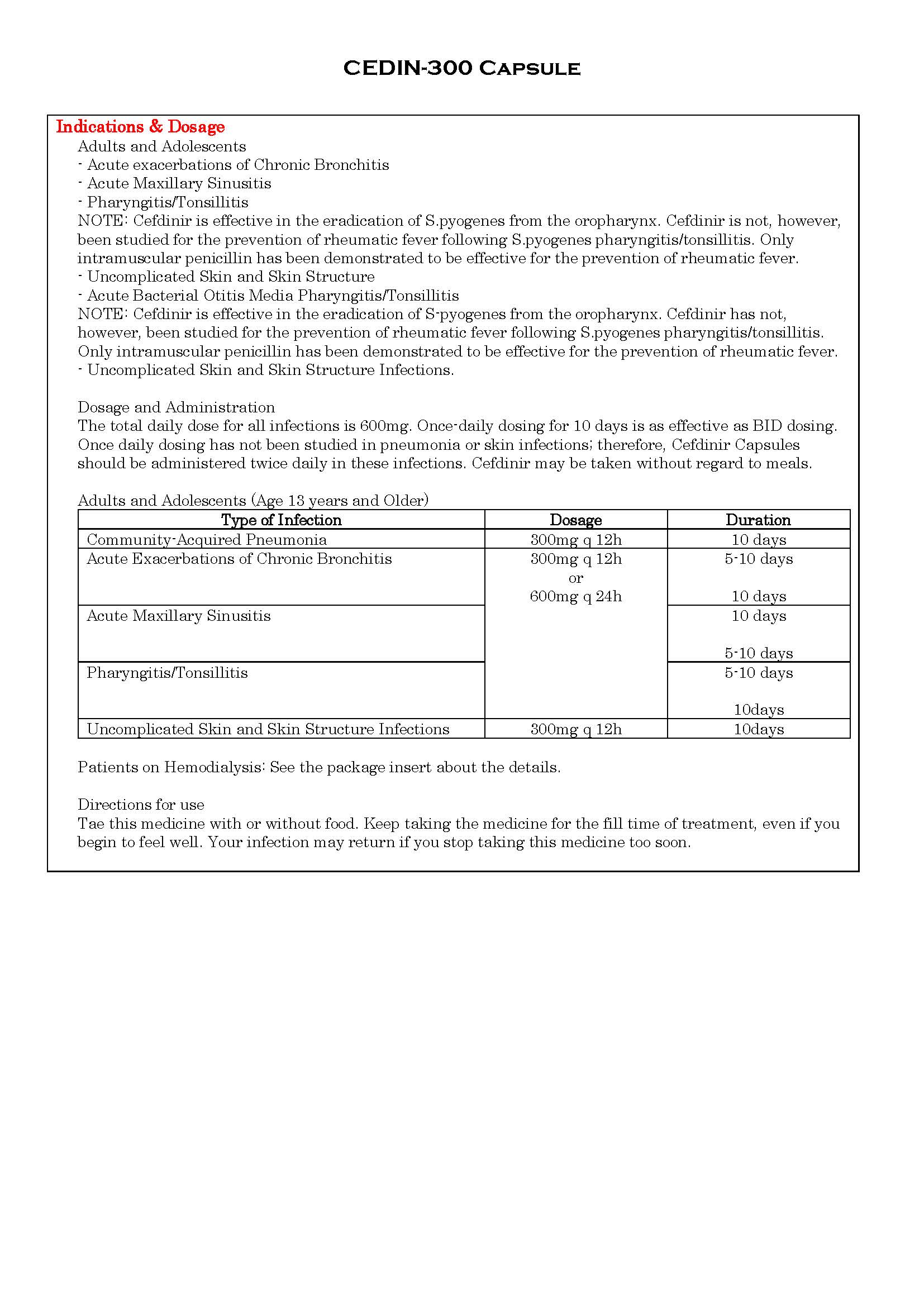
-
ហាមប្រើ
In patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin class of antibiotics.
-
ផលរំខាន
Diarrhea, Yeast infection, Headache, rashes, Vomiting, and Stomach pain are common adverse effects.
Serious side effects
Blood in stools
Severe or watery diarrhea
Unusual headaches
Blurred vision
Unexplained rash
Itchy skin
Hives
Wheezing
Difficulty breathing
Swelling of the throat
Peeling of the skin
Rare side effects
Serious allergic reaction, indigestion bloody diarrhea, loss of appetite (anorexia), heart failures, gas inflammation of the vagina (vaginitis), chest pain, constipation, high blood pressure (hypertension). Increased rate of red blood cell destruction (hemolytic anemia). Reduced amount of platelets in the blood (thrombocytopenia), liver failure, kidney failure and serious intestinal infection (enterocolitis).
-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
Antacids containing magnesium or aluminum interfere with the absorption of Cefdinir. If this type of antacid is required during Cefdinir therapy, Cefdinir should be taken at least 2 hours before or after the antacid.
Iron supplements, including multivitamins that contain iron, interfere with the absorption of Cefdinir. If iron supplements are required during Cefdinir therapy, Cefdinir should be taken at least 2 hours before or after the supplement.
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
Pregnancy
This drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Following administration of single 600mg doses, cefdinir was not detected in human breast milk.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
General
Prescribing Cefdinir in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria. As with other broad-spectrum antibiotics, prolonged treatment may result in the possible emergence and overgrowth of resistant organisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate alternative therapy should be administered. Cefdinir, as with other broad-spectrum antimicrobials (antibiotics), should be prescribed with caution in individuals with a history of colitis.
In patients with transient or persistent renal insufficiency (Creatinine Clearance <30mL/min, the total daily dose of Cefdinir should be reduced because high and prolonged plasma concentrations of Cefdinir can result following recommended doses.
Before therapy with cefdinir is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions to cefdinir, other cephalosporins, penicillins, or other drugs. If cefdinir is to be given to penicillin-sensitive patients, caution should be exercised because cross-hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibiotics has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction to cefdinir occurs, the drug should be discontinued. Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require treatment with epinephrine and other emergency measures, including oxygen, intravenous fluids, intravenous antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines, and airway management as clinically indicated.
Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefdinir, and may range in severity from mild-to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is a primary cause of “antibiotic-associated colitis”. After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, appropriate therapeutic measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to drug discontinuation alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation, and treatment with an antibacterial drug clinically effective against Clostridium difficile.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
Cefdinir is bactericidal and has the same mode of action as other beta-lactam antibiotics (such as penicillins) but is less susceptible to penicillinases. It disrupts the synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls. The peptidoglycan layer is important for cell wall structural integrity. The final transpeptidation step in the synthesis of the peptidoglycan is facilitated by transpeptidases known as penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). PBPs bind to the D-Ala-D-Ala at the end of mucopeptides (peptidoglycan precursors) to crosslink the peptidoglycan. Beta-lactam antibiotics mimic the D-Ala-D-Ala site, thereby competitively inhibiting PBP crosslinking of peptidoglycan. This leads to the death of the bacteria.
Cefdinir is active against a very wide spectrum of bacteria, including:
Aerobic Gram-Positive Microorganisms
Staphylococcus aureus (including beta-lactamase producing strains)
NOTE: Cefdinir is inactive against methicillin-resistant staphylococci.
Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only)
Streptococcus pyogenes
Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms
Haemophilus influenzae (including beta-lactamase producing strains)
Haemophilus parainfluenzae (including beta-lactamase producing strains)
Moraxella catarrhalis (including beta-lactamase producing strains)
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. (See the package insert.)
Aerobic Gram-Positive Microorganisms
Staphylococcus epidermidis (methicillin-susceptible strains only)
Streptococcus agalactiae
Viridans group streptococci
NOTE: Cefdinir is inactive against Enterococcus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus species.
Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms
Citrobacter diversus
Escherichia coli
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Proteus mirabilis
NOTE: Cefdinir is inactive against Pseudomonas and Enterobacter species.
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
