ACNEBOSTON Capsule
ក្រុមហ៊ុនផលិតឱសថ:
Boston Vietnam Pharmaceutical Joint Stock Company, Vietnam
- សារធាតុសកម្ម
- ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
- ហាមប្រើ
- ផលរំខាន
- អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
- ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
- ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
- សកម្មភាពឱសថ បរិយាយប័ណ្ណឱសថ
-
សារធាតុសកម្ម
Isotretinoin 10mg
-
ប្រសិទ្ធិភាពព្យាបាល និង កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់
INDICATIONS
Severe forms of acne, such as (nodular or conglobate ance or acne at risk of permanent scarring) resistant to adequate courses of standard therapy with systemic anti-bacterials and topical therapy.
DOSAGE
- Isotretinoin should only be prescribed by or under the supervision of physicians with expertise in the use of systemic retinoids for the treatment of severe ance and a full understanding of the risks of isotretinoin therapy and monitoring requirements.
- The capsules should be taken with food once or twice daily.
Paediatric Population
-ACNEBOSTON should not be used for the treatment of prepuberal acne and is not recommended in children less than years of age due to a lack of data on efficacy and safety.
Adults including adolescents and the elderly:
- Isotretinoin therapy should be started at a dose of 0.5-1mg/kg daily. The therapeutic response to isotretinoin and some of the adverse effects are dose-related and vary between patients. This necessitates individual dosage adjustment during therapy.
- A treatment course of 16-24 weeks is normally sufficient to achieve remission.
Patients with renal impairment:
- In patients with severe renal insufficiency treatment should be started at a lower dose (e.g. 10 mg/day). The dose should then be increased up to 1 mg/kg/day or until the patient is receiving the maximum tolerated dose.
Patients with intolerance:
- In patients who show severe intolerance to the recommended dose, treatment may be continued at a lower dose with the consequences of a longer therapy duration and a higher risk of relapse. In order to achieve the maximum possible efficacy in these patients the dose should normally be continued at the highest tolerated dose.
ADMINISTRATION
ISOTRETINOIN is administered orally.
-
ហាមប្រើ
ISOTRETINOIN is contraindicated:
+ Hypersensitivity to isotretinoin or to any of the excipients listed.
+ Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
+ Women of childbearing potential unless all of the following condition are meet. (see warning and precautions).
+ Hepatic insufficiency.
+ Excessively elevated blood lipid values.
+ Hypervitaminosis A.
+ Concomitant treatment with tetracyclines.
-
ផលរំខាន
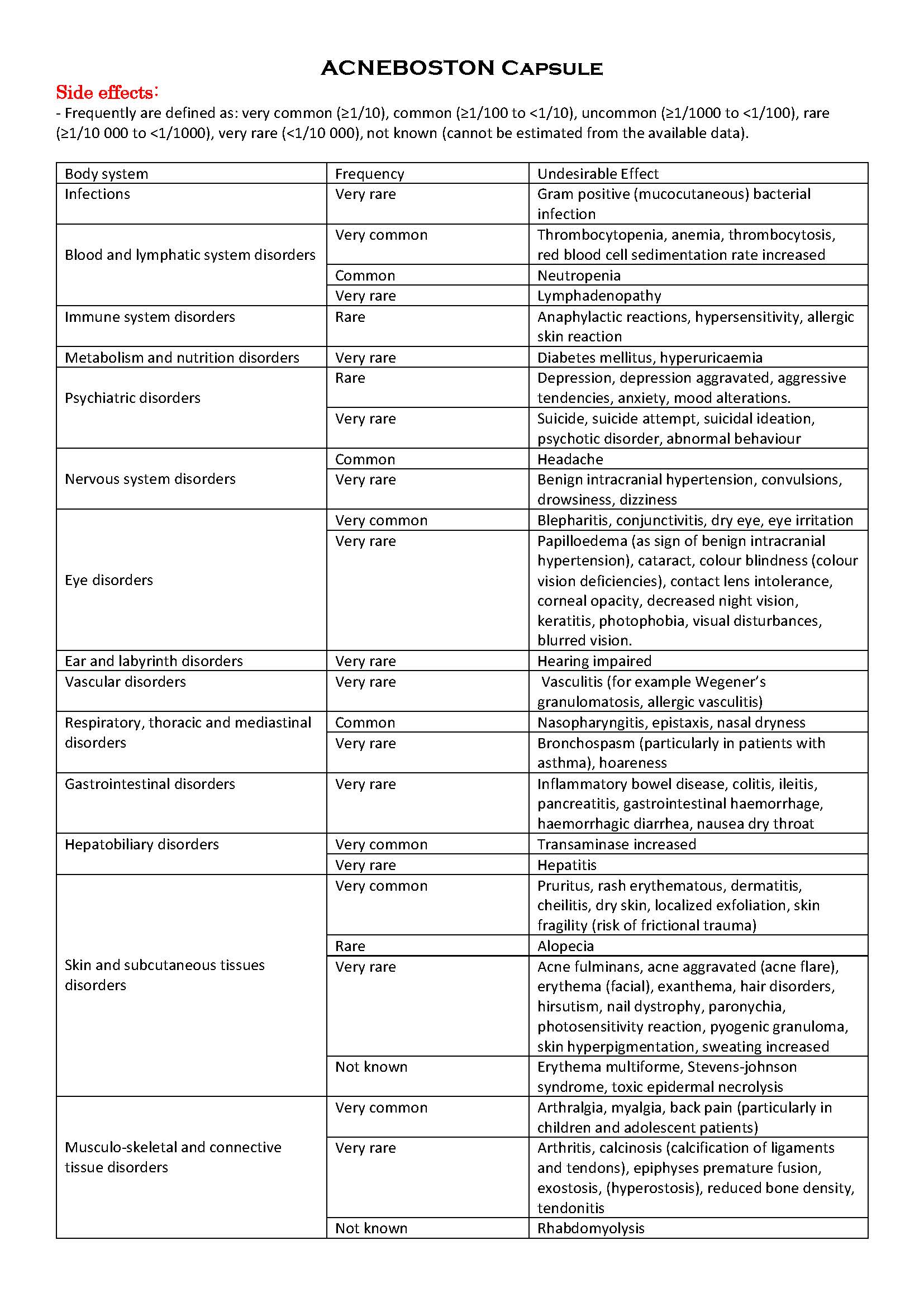

-
អន្តរប្រតិកម្ម
・Vitamin A: Patients should not take vitamin A as concurrent medication due to the risk of developing hypervitaminosis A.
・Tetracyclines: Cases of benign intracranial hypertension have been reported with concomitant use of isotretinoin and tetracyclines. Therefore, concomitant treatment with tetraclines must be avoided.
・Concurrent administration of isotretinoin with topical keratolytic or exfoliative anti-acne agents should be avoided as local irritation may increase.
-
ស្ត្រីមានផ្ទៃពោះ និង ស្ត្រីបំបៅដោះកូន
Pregnancy
- Isotretinoin must not be used by female patients who are pregnancy or may become pregnant.
- The foetal malformations associated with exposure to isotretinoin include central nervous system abnormalities (hydrocephalus, cerebellar malformation/abnormalities, microcephaly), facial dysmorphia, cleft palate, external ear abnormalities (absence of external ear, small or absent external auditory canals), eye abnormalities (microphthalmia), cardiovascular abnormalities (conotruncal malformations such as tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of great vessels, septal defects), thymus gland abnormality and parathyroid gland abnormalities, There is also an increased incidence of spontaneous abortion.
- If pregnancy occurs in a woman treated with isotretinoin, treatment must be stopped and the patient should be referred to a physician specialised or experienced in teratology for evaluation and advice.
Lactation
- Isotretinoin is highly lipophilic, therefore the passage of isotretinoin into human milk is very likely. Due to the potential for adverse effects in the child exposed via mothers' milk, Isotertinoin is contraindicated during breast-feeding.
-
ការប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នជាពិសេស
Isotretinoin is teratogenic
Therefore, it should be contraindicated in women of childbearing potential unless all of the
Following conditions of the Pregnancy Prevention Programme are met:
+ She has severe acne (such as nodular or conglobate acne or acne at risk of permanent scarring) resistant to adequate courses of standard therapy with systemic anti-bacterials and topical therapy.
+ She understands the teratogenic risk.
+ She understands the need for rigorous follow-up, on a monthly basis
+ She understands and accepts the need for effective contraception, without interruption, 1 month before starting treatment, throughout the duration of treatment and 1 month after the end of treatment. At least one and preferably two complementary forms of contraception including a barrier method should be used.
+ Even if she has amenorrhea she must follow all of the advice on effective contraception.
+ She should be capable of complying with effective contraceptive measures.
+ She is informed and understands the potential consequences of pregnancy and the need to rapidly consult if there is a risk of pregnancy.
+ She understands the need and accepts to undergo pregnancy testing before, during and 5 weeks after the end of treatment.
+ She has acknowledged that she has understood the hazards and necessary precautions associated with the use of isotretinoin.
These conditions also concern women who are not currently sexually active unless the prescriber considers that there are compelling reasons to indicate that there is no risk of pregnancy.
The prescriber must ensure that:
+ The patient complies with the conditions for pregnancy prevention as listed above, including confirmation that she has an adequate level of understanding.
+ The patient has acknowledged the aforementioned conditions.
+ The patient has used at least one and preferably two methods of effective contraception including a barrier method for at least 1 month prior to starting treatment and is continuing to use effective contraception throughout the treatment period and for at least 1 month after cessation of treatment.
+ Negative pregnancy test results have been obtained before, during and 5 weeks after the end of treatment. The dates and results of pregnancy tests should be documented,
Controception
- Female patients must be provided with comprehensive information on pregnancy prevention and should be referred for contraceptive advice if they are not using effective contraception.
- As a minimum requirement, female patients at potential risk of pregnancy must use at least one effective method of contraception. Preferably the patient should use two complementary forms of contraception including a barrier method.
- Contraception should be continued for at least 1 month after stopping treatment with isotretinoin, even in patients with amenorrhea.
Pregnancy testing
- According to local practice, medically supervised pregnancy tests with a minimum sensitivity of 25 mlU/mL are recommended to be performed in the first 3 days of the menstrual cycle, as follows.
Prior to starting therapy:
- In order to exclude the possibility of pregnancy prior to starting contraception, it is recommended that an initial medically supervised pregnancy test should be performed and its date and result recorded. In patients without regular menses, the timing of this pregnancy test should reflect the sexual activity of the patient and should be undertaken approximately 3 weeks after the patient last had unprotected sexual intercourse. The prescriber should educate the patient about contraception.
- A medically supervised pregnancy test should also be performed during the consultation when isotretinoin is prescribed or in the 3 days prior to the visit to the prescriber, and should have been delayed until the patient had been using effective contraception for at least 1 month. This test should ensure the patient is not pregnant when she starts treatment with isotretinoin.
Follow-up visits:
Follow-up visits should be arranged at 28 day intervals. The need for repeated medically supervised pregnancy tests every month should be determined according to local practice including consideration of the patient's sexual activity and recent menstrual history (abnormal menses, missed periods or amenorrhea). Where indicated, follow-up pregnancy tests should be performed on the day of the prescribing visit or in the 3 days prior to the visit to the prescriber.
End of treatment
- Five weeks after stopping treatment, women should undergo a final pregnancy test to exclude pregnancy.
Male patients:
- The available data suggest that the level of maternal exposure from the semen of the patients receiving isotretinoin, is not of a sufficient magnitude to be associated with the teratogenic effects of isotretinoin.
Male patients should be reminded that they must not share their medication with anyone, particularly not females.
Additional precautions:
- Patients should be instructed never to give this medicinal product to another person and should not donate blood during therapy and for 1 month following discontinuation of isotretinoin because of the potential risk to the foetus of a pregnant transfusion recipient.
Psychiatric disorders
- Depression, depression aggravated, anxiety, aggressive tendeneics, mood alterations, psychotic symptoms, and very rarely, suicidal ideation. suicide attempts and suicide have been reported in patients treated with isotretinoin. Particular care needs to be taken in patients with a history of depression and all patients should be monitored for signs of depression and referred for appropriate treatment if necessary. However, discontinuation of isotretinoin may be insufficient to alleviate symptoms and therefore further psychiatric or psychological evaluation may be necessary.
Skin and subcutaneous tissues disorders
- Acute exacerbation of acne is occasionally seen during the initial period but this subsides with continued treatment, usually within 7- 10 days, and usually does not require dose adjustment.
- Exposure to intense sunlight or to UV rays should be avoided. Where necessary a sun protection product with a high protection factor of at least SPF 15 should be used.
- Aggressive chemical dermabrasion and cutaneous laser treatment should be avoided in patients on isotretinoin for a period of 5-6 months after the end of the treatment because of the risk of hypertrophic scarring in atypical areas and more rarely post inflammatory hyper or hypopigmentation in treated areas. Wax depilation should be avoided in patients on isotretinoin for at least a period of 6 months after treatment because of the risk of epidermal stripping.
- Concurrent administration of isotrctinoin wi1h topical kcratolytic or exfoliative nnti·acne agents should be avoided as local irritation may increase .
- Isotretinoin is likely to cause dryness of the skin and lips, so patients should be avoided to use a skin moisturising oilment or cream and a lip balm from the start of treatment. There have been post-marketing reports of severe skin reactions (e.g. erythema multiforme (EM), StevensJohnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)) associated with isotretinoin use. Patients should be monitored closely for severe skin reactions, and discontinuation of isotretinoin should be considered if warranted.
Allergic reactions
- Anaphylactic reactions have been rarely reported. Allergic cutaneous reactions are reported
infrequently. Serious cases of allergic vasculitis, often with purpura (bruises and red patches) of the extremities and extracutaneous involvement have been reported. Severe allergic reactions necessitate interruption of therapy and careful monitoring.
Eye disorders
- Dry eyes, corneal opacities, decreasd night vision and keratitis usually resolve after discontinuation of therapy. Dry eyes can be helped by the application of a lubricating eye ointment or by the application of tear replacement therapy. Patients experiencing visual difficulties should be referred for an expert opthalmological opinion. Withdrawal of isotretinion may be necessary.
Musculo-skeletal and connective tissue disorders
- Myalgia, arthralgia and increased serum creatine phosphokinase values have been reported in patients receiving isotretinoin, particular in those undertaking vigrous physical activity. In some cases, this may progress to potentially life threatening rhabdomyolysis.
- Bone changes including premature epiphyseal closure, hyperostosis, and calcification of tendons and ligaments have occurred after several years of administration at very high doses for treating disorders of keratinisation. The dose levels, duration of treatment and total cumulative dose in these patients generally far exceeded those recommended for the treatment of acne.
Benign intracranial hypertension
- Cases of benign intracranial hypertension have been reported, some of which involved concomitant use of tetracyclines. Signs and symtomps of benign intracranial hypertension include headache, nausea and vomiting, visual disturbances and papilloedema. Patients who develop benign intracranial hypertension should discontinue isotretinoin immediately.
Hepatobiliary disorders
- Liver enzymes should be checked before treatment, 1 month after the start of treatment, and subsequently at 3 monthly intervals unless more frequent monitoring is clinically indicated. Transient and reversible increases in liver transaminases have been reported. However, in the event of persistent clinically relevant elevation of transaminase levels, reduction of the dose or discontinuation of treatment should be considered.
Renal insufficiency
- Renal insufficiency and renal failure do not affect the pharmacokinetics of isotretinoin. Therefore, isotretinoin can be given to patients with renal insufficiency. However, it is recommended that patients are started on a low dose and titrated up to the maximum tolerated dose.
Lipid Metabolism
- Serum lipids (fasting values) should be checked before treatment, 1 month after the start of treatment, and subsequently at 3 monthly intervals unless more frequent monitoring is clinically indicated. Elevated serum lipid values usually return to normal on reduction of the dose or discontinueation of treatment and may also respond to dietary measures.
- Isotretinoin has been associated with an increase in plasma triglyceride levels. Isotretinoin should be discontinued if hypertriglyceridaemia cannot be controlled at an acceptable level or if symptoms of pancreatitis occur. Levels in excess of 800 mg/dL or 9 mmol/L are sometimes associated with acute pancreastitis, which may be fatal.
Gastrointestinal disorders
- Isotretinoin has been associated with inflammatory bowel disease (including regoinal ileitis) in patients without a prior history of intestinal disorders. Patients experiencing severe (hemorrhagic) diarrhoea should discontinue isotretinoin immediately.
High Risk Patients
- In patients with diabetes, obesity, alcoholism or a lipid metabolism disorder undergoing treatment with isotretinoin, more frequent checks of serum values for lipids and/or blood glucose may be necessary.
-
សកម្មភាពឱសថ
Isotretinoin is a stereoisomer of all-trans retinoic acid (tretinoin). The exact mechanism of action of isotretinoin has not yet been elucidated in detail, but it has been established that the improvement observed in the clinical picture of severe acne is associated with suppression of sebaceous gland activity and a histologically demonstrated reduction in the size of the sebaceous glands. Furthermore, a dermal anti-inflammatory effect of isotretinoin has been established.
*ព័ត៌មានឱសថត្រូវបានរៀបរៀងដោយ អ៊ីម៉ាតុគឹ មេឌីក (ខេមបូឌា) ដោយផ្អែកលើប្រភពព័ត៌មានខាងក្រោម។ សម្រាប់ព័ត៌មានលម្អិត សូមស្វែងរកនៅក្នុងក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថនីមួយៗ ឬ សាកសួរទៅកាន់ក្រុមហ៊ុនឱសថឬតំណាងចែកចាយនៃឱសថនីមួយៗ។
ប្រភពព័ត៌មាន៖
- ក្រដាសព័ត៌មាននៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំនាញវេជ្ជសាស្ត្រដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន (Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency, Pmda): https://www.pmda.go.jp
- ព័ត៌មានសង្ខេបនៃឱសថសម្រាប់អ្នកជំងឺដែលប្រើប្រាស់នៅប្រទេសជប៉ុន: http://www.rad-ar.or.jp
